Fig. 4.
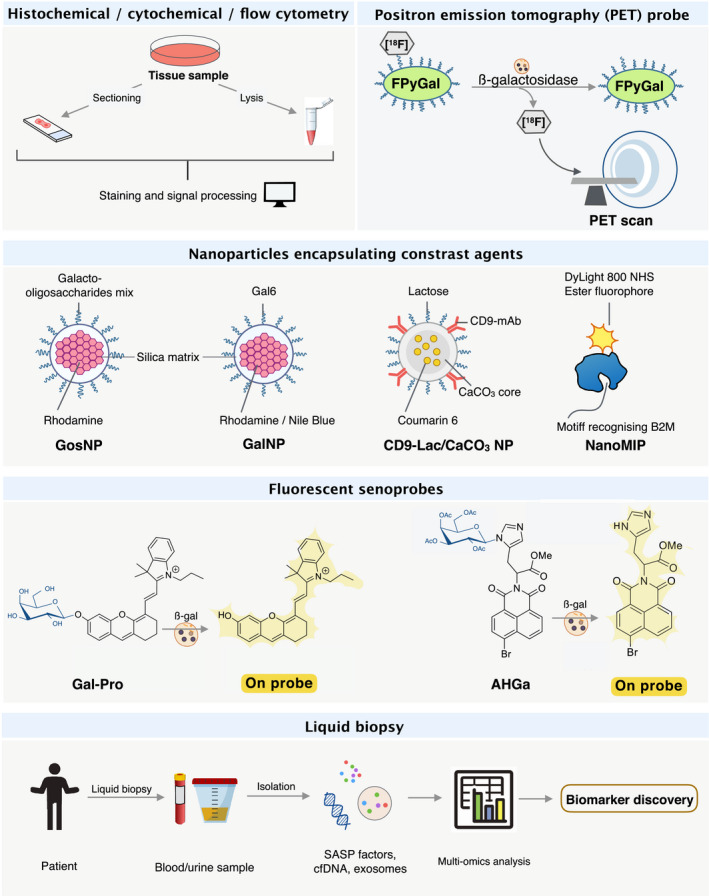
Novel approaches for in vivo senescence detection. In addition to conventional detection methods relying on IHC detection of multiple senescence biomarkers in deep‐frozen or fixed tissues, recent development of approaches combining histochemical, cytochemical and flow cytometry offer higher efficiency for senescence detection in fresh tissues. The fine tuning of nanoparticles for recognising senescent cells strengthens further the targeted delivery of cargoes, that is, image contrasting agents, into senescent tumour cells. Avoiding potential cytotoxicity, OFF‐ON Senoprobes facilitate the real‐time detection and tracking of living senescent cells with elevated SAβG activity. In the human setting, the senescent‐specific PET probe FPyGal may be used to assess senescence burden within tumours pre‐ and post‐treatment, which would provide valuable information in the design of therapeutic strategies and inpatient response. The emerging field of cell‐free DNA (cfDNA) analysis in liquid biopsy provides the least invasive senescence detection tool that is also usable in large‐scale and longitudinal patient screening and monitoring. B2M, β2 microglobulin; nanoMIP, molecular imprinted nanoparticle; NP, nanoparticle; SAβG, senescence‐associated β‐galactosidase.
