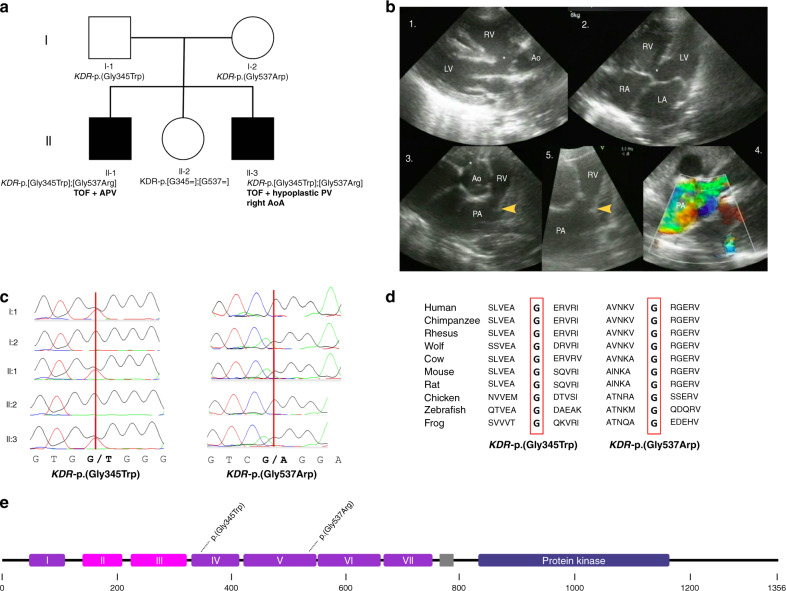
Fig. 1. Identification of compound heterozygous KDR variants in a family with tetralogy of Fallot (TOF).
(a) Pedigree of index family. The two affected children are marked with black symbols, the unaffected parents and sibling with white symbols. Genotypes are shown beneath. (b) Echocardiographic images of II-1 before cardiac surgery. 1: Parasternal long-axis view showing the large malalignment ventricular septal defect (VSD) (*) and the overriding of the aorta. 2: Four chamber view showing the VSD. 3: Short-axis view of the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT), the dysplastic pulmonary valve (arrow) and dilated main pulmonary artery. 4: Color Doppler image showing turbulent flow (yellow-green) over the dysplastic valve consistent with a significant stenosis. 5: Detail of the RVOT, dysplastic pulmonary valve, and dilated PA. Note the dysplastic valve leaflets and small annulus. (c) Sanger sequencing chromatograms confirming a compound heterozygous inheritance in the two affected children. (d) Conservation of glycine residues at amino acid position 345 and 537 across species. (e) Location of KDR-p.(Gly345Trp) and KDR-p.(Gly537Arg) on the protein VEGFR2 subdomains are based on Roskoski.20 Ao aorta, AoA aortic arch, APV absent pulmonary valve, LA left atrium, LV left ventricle, PA pulmonary artery, PV pulmonary valve, RA right atrium, RV right ventricle.