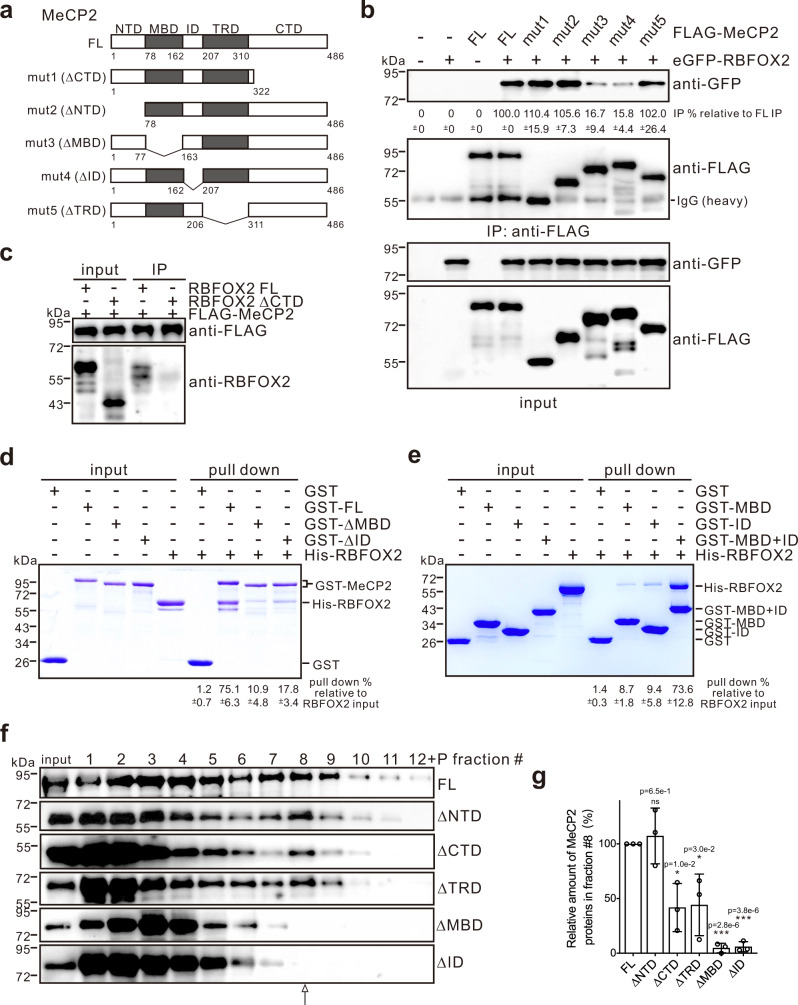
Fig. 2. MeCP2 interacts with RBFOX2 directly, and its MBD and ID are required for its association with RBFOX2/LASR complex.
a Schematic representation of FL and deletion mutants of MeCP2. b Co-IP assays performed by anti-FLAG antibody in HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-tagged FL or deletion mutants of MeCP2 in the presence of nuclease and analyzed by western blotting with anti-GFP antibody. The average percentages of IP efficiency with standard deviations relative to the FL MeCP2 IP efficiency are shown below the gel (n = 3 biologically independent experiments). c IP assays performed by anti-FLAG antibody in HEK293T cells expressing RBFOX2 FL or its ΔCTD mutant in the presence of nuclease and analyzed by western blotting with anti-RBFOX2 antibody. d Representative results for GST pull-down analysis of the interactions between GST-tagged FL, ΔMBD, and ΔID of MeCP2 proteins and His-tagged RBFOX2. e Representative results for GST pull-down analysis of the interactions between GST-tagged MBD, ID, and MBD + ID of MeCP2 proteins and His-tagged RBFOX2. The average percentages of pulled down RBFOX2 relative to the input with standard deviations are shown below the gel in d, e (n = 3 biologically independent experiments). f Representative results for sedimentation profiles of the FL and mutant MeCP2 proteins in the HMW extract from HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-tagged MeCP2 proteins on 10–50% glycerol gradients. The FL and mutant MeCP2 proteins were detected by western blot analysis with anti-FLAG antibody. g Quantitation of the relative amount of MeCP2 proteins associated with Rbfox/LASR. The average percentages of MeCP2 proteins in fraction #8 to the sum of those in total fractions are normalized to that of FL MeCP2. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3 biologically independent experiments, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, two-sided Student’s t test). Source data are provided as a Source data file.