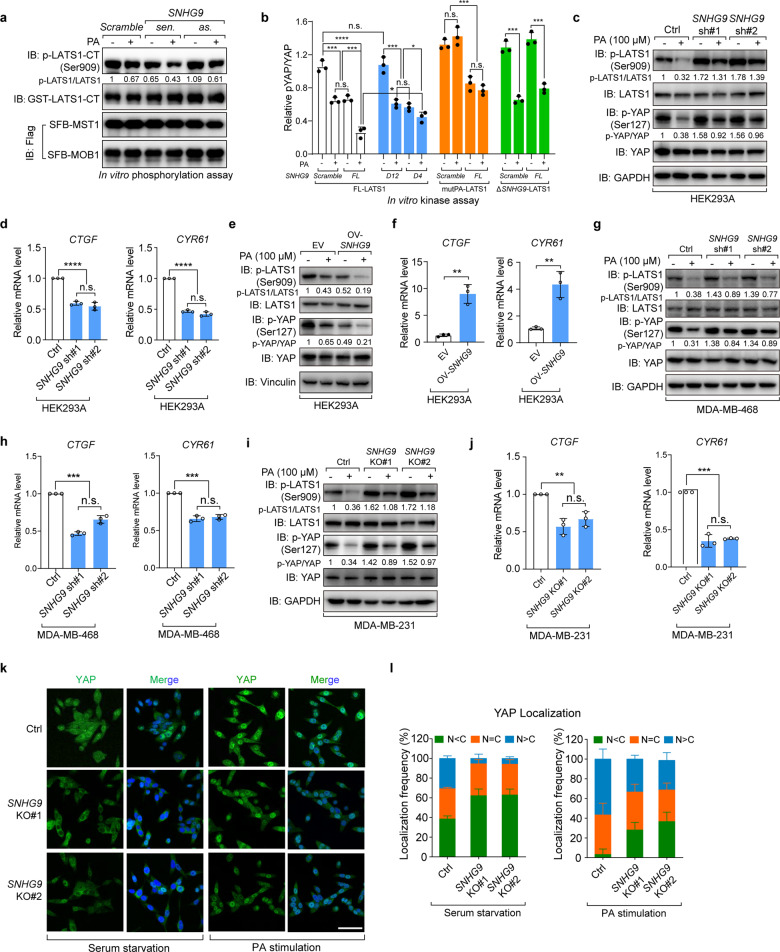
Fig. 3. SNHG9 promotes PA-mediated LATS1 inactivation.
a In vitro LATS1 phosphorylation assay using recombinant LATS1-CT, eukaryotic purified MST1, MOB1 proteins and in vitro-transcribed RNA transcripts as indicated in NETN buffer with the presence of 500 µM ATP. Bacterially purified GST-LATS1-CT protein was used as the substrate. Immunoblots were used to detect the p-LATS1 (S909). b Flag-FL-LATS1, Flag-mutPA-LATS1 and Flag-ΔSNHG9-LATS1 were expressed in HEK293A cells, respectively, and purified by anti-Flag M2 magnetic beads. MOB1 and MST forming complex with above proteins were also pulled down. In vitro kinase assay was performed using above proteins, in vitro-transcribed SNHG9-FL, SNHG9-D12, SNHG9-D4 transcripts and PA as indicated in NETN buffer with 500 µM ATP. Bacterially purified GST-YAP protein was used as the substrate. Densitometry analysis of p-YAP/YAP levels (means ± SEM, n = 3 experiments) was shown. (n.s., not significant; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, Student’s t-test). c, d Knockdown of SNHG9 largely revoked PA-mediated inhibition on the phosphorylation of LATS1 and YAP. Serum-starved wild-type and SNHG9 KD HEK293A cells were treated with PA (100 μM) for 1 h, and the levels of p-LATS1 (S909), p-YAP (S127) were detected using immunoblotting (c). Serum-starved wild-type and SNHG9 KD HEK293A cells were treated with PA (100 μM) for 4 h, and the expression levels of YAP target genes including CTGF and CYR61 were detected by qRT-PCR (d). Error bars, SEM of three independent experiments (n.s., not significant; ****P < 0.0001, Student’s t-test). e, f Overexpression of SNHG9 promotes PA-mediated inhibition on the phosphorylation of LATS1 and YAP. Serum-starved wild-type and SNHG9-overexpressed HEK293A cells were treated with PA (100 μM) for 1 h, and the levels of p-LATS1 (S909), p-YAP (S127) were detected using immunoblotting (e). Serum-starved wild-type and SNHG9-overexpressed HEK293A cells were treated with PA (100 μM) for 4 h, and the expression levels of YAP target genes including CTGF and CYR61 were detected by qRT-PCR (f). Error bars, SEM of three independent experiments (**P < 0.01, Student’s t-test). g, h Knockdown of SNHG9 largely revoked PA-mediated inhibition on the phosphorylation of LATS1 and YAP. Serum-starved wild-type and SNHG9 KD MDA-MB-468 cells were treated with PA (100 μM) for 1 h, and the levels of p-LATS1 (S909), p-YAP (S127) were detected using immunoblotting (g). Serum-starved wild-type and SNHG9 KD MDA-MB-468 cells were treated with PA (100 μM) for 4 h, and the expression levels of YAP target genes including CTGF and CYR61 were detected by qRT-PCR (h). Error bars, SEM of three independent experiments (n.s., not significant; ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test). i, j Knockout of SNHG9 largely revoked PA-mediated inhibition on the phosphorylation of LATS1 and YAP. Serum-starved wild-type and SNHG9 KO MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with PA (100 μM) for 1 h, and the levels of p-LATS1 (S909), p-YAP (S127) were detected using immunoblotting (i). Serum-starved wild-type and SNHG9 KO MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with PA (100 μM) for 4 h, and the expression levels of YAP target genes including CTGF and CYR61 were detected by qRT-PCR (j). Error bars, SEM of three independent experiments (n.s., not significant; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test). k, l SNHG9 KO largely revoked PA-mediated YAP nuclear translocation. Serum-starved wild-type and SNHG9 KO MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with PA (100 μM) for 1 h. Representative images of YAP subcellular localization were shown (k). Cells from five different fields were randomly selected and quantified for YAP localization (l). Scale bar, 50 μm. Error bars, SEM of three independent experiments.