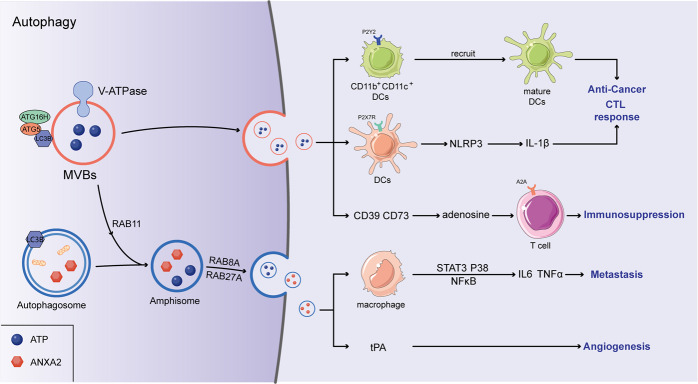
Fig. 1. Autophagy and the release of immune-related EVs.
The autophagy-associated complex (ATG5–ATG16) translocalized to MVBs and dissociated vacuolar proton pumps (V-ATPase) from MVBs, in which the acidification of the MVBs lumen was inhibited. Ultimately, the secretion of EVs augmented via MVBs–plasma membrane (PM) fusion. In addition, amphisomes were formed by the fusion of autophagosomes and MVBs, which accelerated the EVs release controlled by RAB8A and RAB27A. Immunoregulatory factors including ANXA2 and ATP were contained in EVs, ANXA2 can induce an increased secretion of TNFα and IL6 by activating the STAT3, p38, and NF-κB pathways in macrophages. In addition, ANXA2 promotes tPA-dependent angiogenesis. ATP can promote the differentiation of CD11b+CD11c+Ly6Chigh cells into mature DCs by binding with purinergic receptor P2Y2, and upregulate the IL-1β production through NLRP3 inflammasome, ultimately stimulating the activation of anti-tumor CTL responses. However, adenosine can be converted from ATP hydrolyzed by CD39 and CD73, further inhibiting T-cell activation through binding with the adenosine A(2 A) receptor.