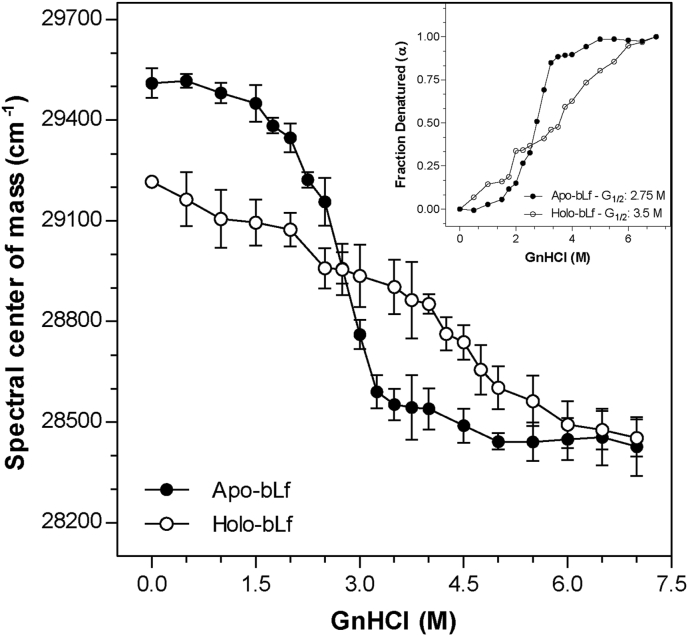
Figure 1.
GnHCl-induced denaturation of bLf monitored using intrinsic fluorescence emission. In order to verify the effects of GnHCl and to obtain total denaturation of bLf, increasing concentrations of the compound was added to the protein (0.5 M–7.0 M). The protein was diluted in standard buffer to a final concentration of 500 μg/mL. The spectral center of mass was measured at various GnHCl concentrations. Fluorescence excitation wavelength: 280 nm; emission wavelength range: 300 nm–420 nm. The inset represents the denatured fraction of apo- and holo-bLf in the presence of GnHCl. Data were obtained from three independent experiments and plotted as mean ± SD. Differences in means compared to control were not significant up to 2 M GnHCl for holo-bLf and up to 1.5 M GnHCl for apo-bLf. For all other conditions, differences from the respective controls were significant. Student's t-test showed that the difference between apo- and holo-bLf at 0 M GnHCl was significant (p value = 0.0058).