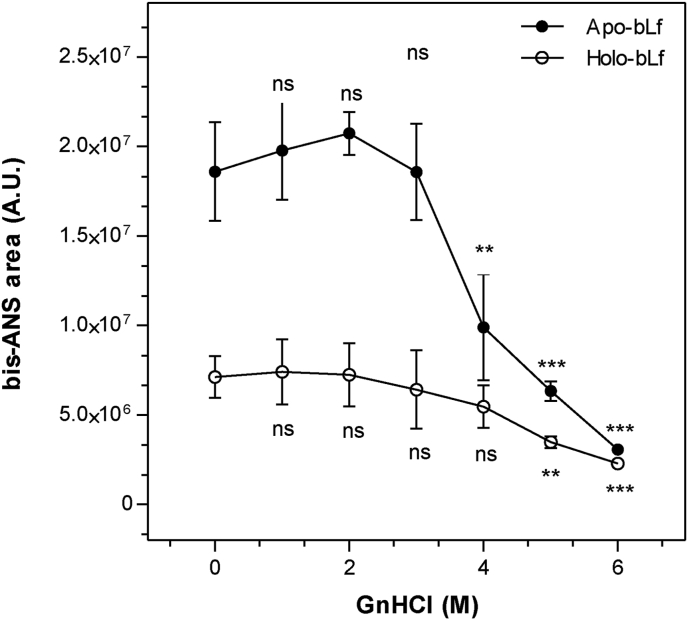
Figure 2.
GnHCl-induced denaturation of bLf monitored using extrinsic bis-ANS fluorescence emission. The hydrophobic bis-ANS probe was used to monitor the denaturation of apo- and holo-bLf in the presence of GnHCl. The bis-ANS concentration used was 40 μM. The protein was diluted in standard buffer to a final concentration of 500 μg/mL. Fluorescence excitation wavelength: 360 nm; emission wavelength range: 400 nm–600 nm. Data were obtained from three independent experiments and plotted as mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA revealed significant differences in means compared to the respective controls, as shown in the figure (∗∗∗, p ≤ 0.001; ∗∗, p ≤ 0.01; ∗, p ≤ 0.05; ns = not significant, p > 0.05). Student's t-test showed differences in means of binding to bis-ANS between apo and holo-bLf, in control condition (p value = 0.0364).