Fig. 2.
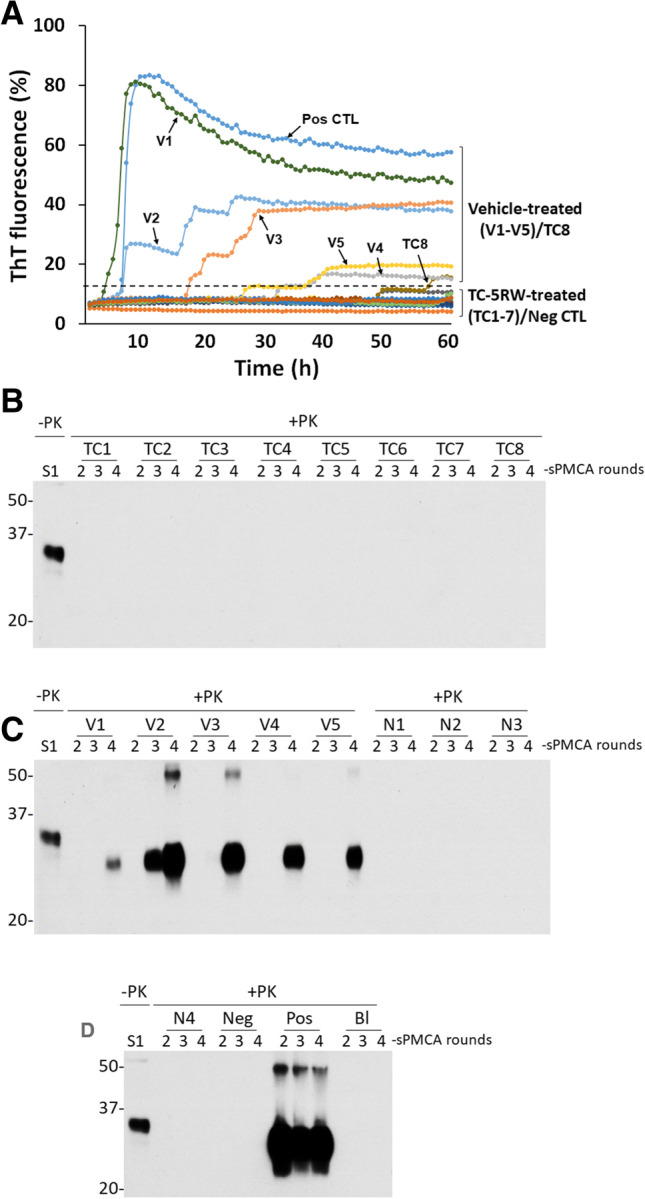
Detection of skin prion-seeding activity in 263 K-infected Tg mice by RT-QuIC and sPMCA. A Blinded RT-QuIC assay of prion-seeding activity in skin samples from 263 K-infected Tg7 mice treated with TC-5RW (TC1-8) or saline (vehicle-treated, V1-5). Pos CTL: positive controls with brain homogenate from a 263 K-infected hamster as the seed; Neg CTL: negative controls with brain homogenate from a healthy hamster as the seed. Dotted line represents the threshold that defines the positive and negative seeding activity based on the average ThT fluorescence of negative controls plus three SD. B Western blotting of blinded sPMCA products of skin samples from 263 K-infected Tg7 mice injected with TC-5RW (TC1-8). Normal brain homogenate without PK treatment was used as a control (S1). C Western blotting of blinded sPMCA products of skin samples from 263 K-infected Tg7 mice given saline (vehicle controls, V1-5) and non-infected Tg7 mouse controls (N1-3). D Western blotting of blinded sPMCA products of skin samples from non-infected Tg7 mouse (N4) as well as with normal control (Neg) and 263 K-infected hamster control (Pos) brain homogenate as seeds and no seeds control (blank: Bl). In the sPMCA experiment, there were 2 sets of positive and negative controls. The infected Tg mice treated with saline (vehicle controls, V1-V5) served as positive controls while uninfected Tg mice (N1-N4) served as negative controls for our animal study. In addition, the 263 K-infected hamster brain homogenates were used as positive controls while both uninfected hamster brain homogenates and sPMCA reaction without seeds (BI) served as negative controls of sPMCA to make sure that sPMCA worked. The sPMCA samples were 2–4 rounds of sPMCA products and were treated with PK prior to Western blotting probing with 3F4
