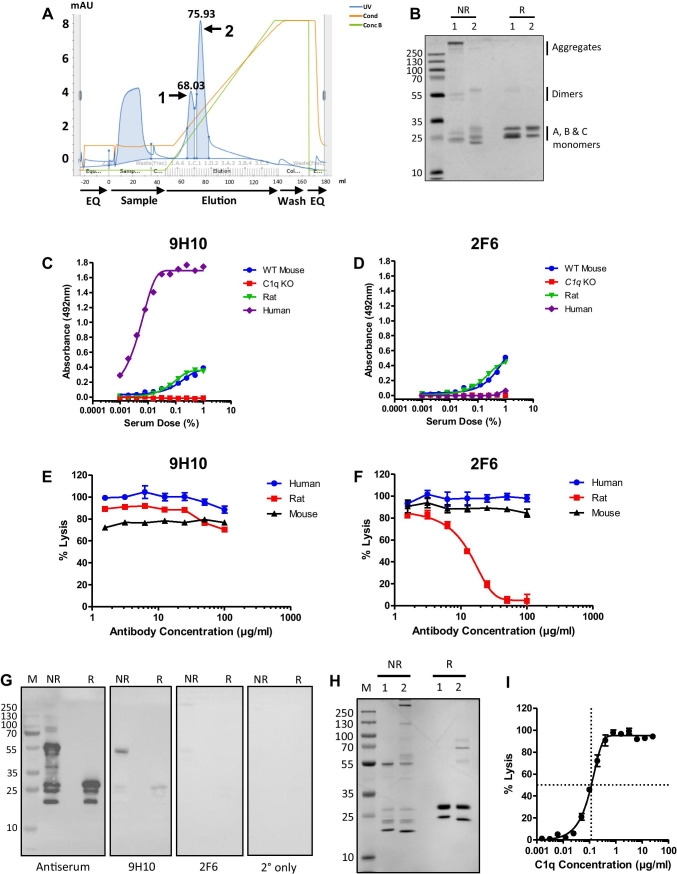
Fig. 1.
Isolation of pure mouse C1q and characterisation of novel monoclonal antibodies. (A) Representative ÄKTA chromatogram from the cation exchange purification of mouse C1q showing 2 peaks. (B) SDS-PAGE of cation exchange fractions (2.5 μg/lane) from peak 1 and peak 2; non-reduced (NR), or reduced with 5% β-mercaptoethanol (R), proteins were stained with Coomassie blue. Peak 1 contained aggregated mouse C1q that reduced to the individual C1q A, B, and C monomers at 31 kDa, 29 kDa, and 26 kDa; peak 2 contained pure mouse C1q with no aggregates that reduced to C1q monomers. (C) C1q sandwich ELISA using 9H10 as capture antibody and polyclonal anti-C1q as detect showing cross-reactivity with mouse, rat, and human C1q. (D) C1q sandwich ELISA using 2F6 as capture antibody and polyclonal anti-C1q as detect showing 2F6 cross-reactivity with mouse and rat C1q but not human C1q. (E, F) Classical pathway haemolytic assays showing that 9H10 had no inhibitory activity towards mouse, rat, or human C1q, while 2F6 inhibited rat C1q, but not mouse or human C1q. (G) Western blot of mouse C1q. Denatured pure C1q (1 μg/lane) under NR and R conditions and Western blotted with mouse anti-C1q antiserum (1:500), 9H10, and 2F6 (2 μg/ml). 9H10 bound the A chain in denatured C1q under both non-reducing and reducing conditions; staining with 2F6 was weak under both conditions. All membranes were exposed together, and for the same time, the images are unmodified from the original .tif files. (H) SDS-PAGE of mouse C1q isolated via IgG affinity followed by cation exchange (1) and 9H10 immunoaffinity purification (2) under both non-reducing and reducing conditions and stained with Coomassie blue. (I) Classical pathway haemolytic assay demonstrating that titration (from 25 μg/ml) of mouse C1q isolated via 9H10 immunoaffinity restored activity to C1q KO serum (25%); 116 ng/ml of mouse C1q was required to restore lysis to 50%