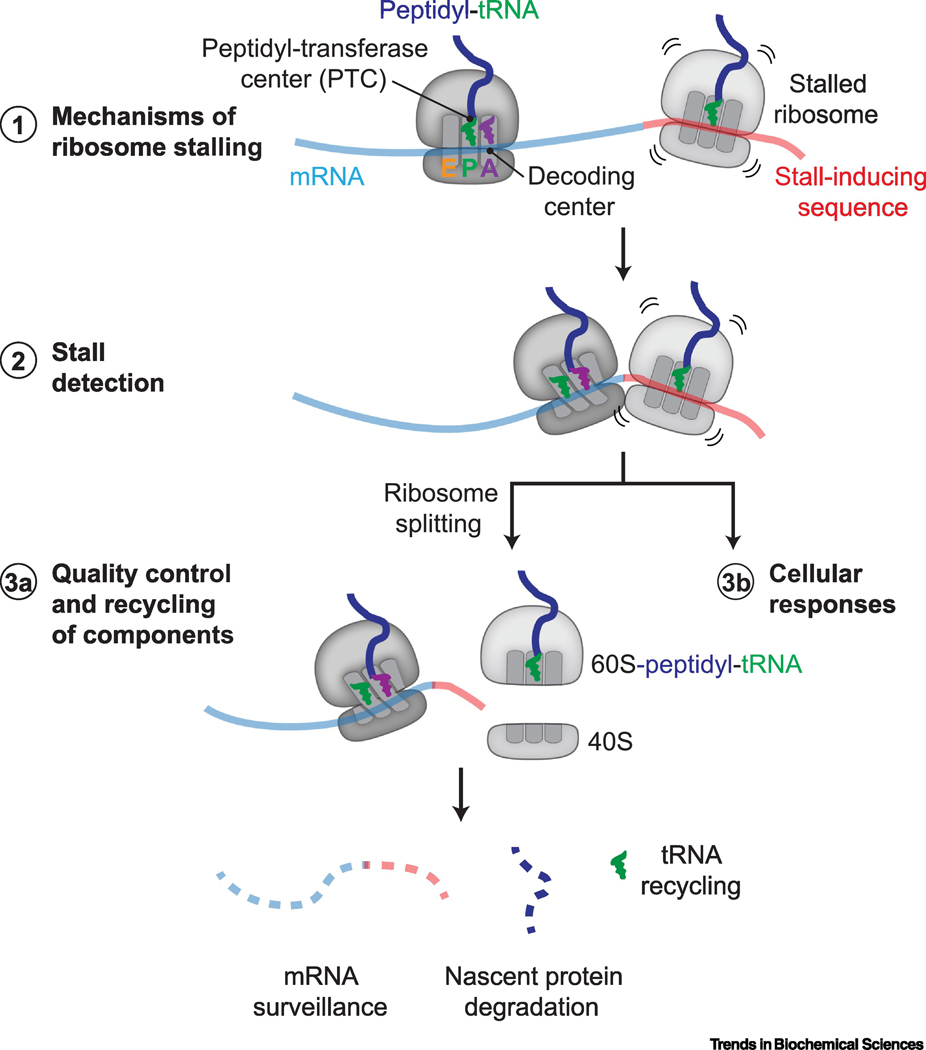
Figure 1 |. Progress on ribosome rescue in eukaryotes.
Recent work has revealed (1) insights into how ribosomes stall while translating specific mRNA sequences (red). The aminoacyl (A), peptidyl (P), and exit (E) tRNA binding sites, decoding center, and peptidyl-transferase center (PTC) on an 80S ribosome are indicated. (2) Ribosome rescue requires factors that specifically detect molecular signatures of ribosome stalling, such as an empty decoding center or ribosome collisions. Ribosome rescue factors activate (3a) local quality control and recycling mechanisms to process individual components of stalled ribosomal complexes and (3b) cellular stress responses to reduce proteotoxic burden.