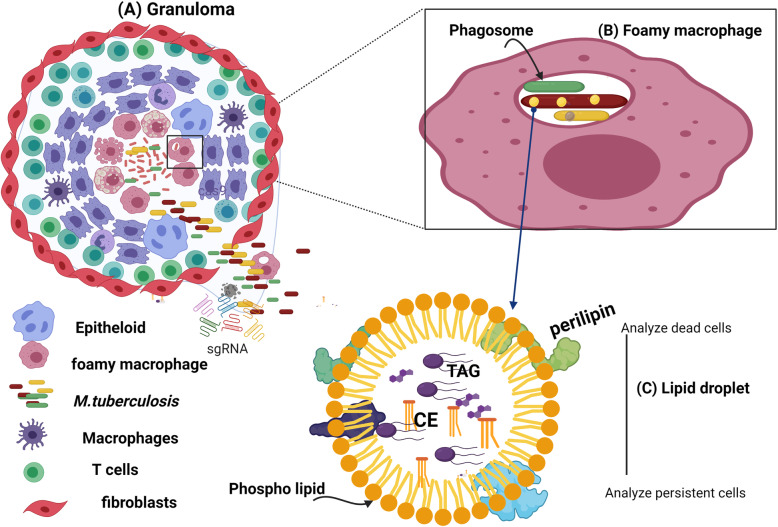
Fig. 1.
A:Necrotic granuloma, B: Foamy macrophages that contain LD-positive Mtb in granuloma tissue, phagocytosed Mtb C: Lipid droplet. A: The necrotic granuloma is a cryptic infectious immunopathological architecture and compacted collection phagocytic cells. It is the hallmark of tuberculosis [24]. Evidence showed that, except macrophages which serve as a feeder for new Mtb infection, innate immunity has only a little role in the initiation of granuloma formation and bacterial virulence factors such as trehalosdimycolate and ESX-1 are the driving factors for priming granuloma formation [25]. Once it is primed, dendritic cells migrate to regional lymph nodes, activate Th cells making the granuloma mature through layering of cells (macrophage, foamy macrophage, epithelioid, T cells and fibroblasts) [25]. The macrophage is the predominant phagocytic cell which occurs in differentiated forms. These are epithelioid, multinucleated giant cells, foamy macrophages and ruffled membrane macrophages [24]. Mtb might be found in the granuloma microenvironment due to rupture of phagosome and foamy macrophages. When the granuloma ruptures Mtb will be seeded to the environment through coughing, sneezing and talking. The metabolism and the level of stress in each microenvironment is different, driving Mtb into at least three distinct phenotypic and metabolic states; actively replicating (green), Lipid droplets (LD) loaded persister phenotype (red) and borderline between the two states (yellow). B: A macrophage that ingests Mtb through phagocytosis may harbor multiple Mtb phenotypes and may become a warehouse of lipid and serving as an energy reserve. These lipid-loaded macrophages are called foamy macrophages). C: Lipid droplets are composed of a hydrophobic core of neutral lipids (triacylglycerol, TAG and cholesterol ester, CE) surrounded by a phospholipid monolayer (phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylinositol (PI) and lyso-phospholipids) decorated with different proteins. LD is an efficient energy storage organelle, as the most compacted and efficient means to store excess lipid in cells. Figures are created with BioRender.com