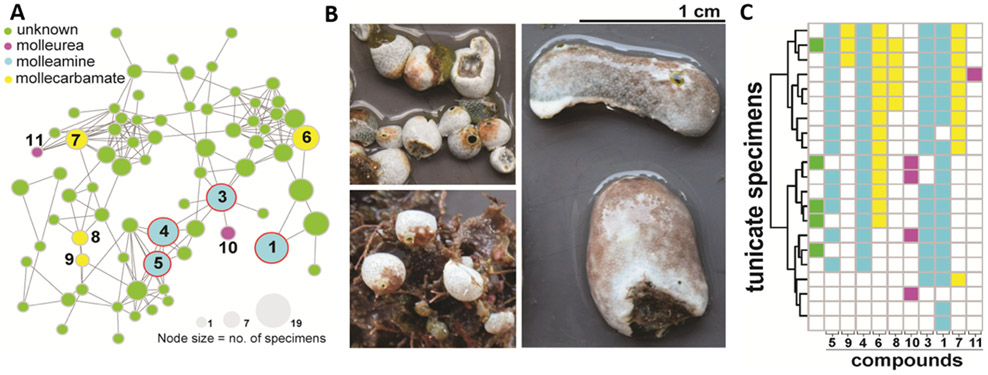
Figure 2.
AEBA-containing metabolites are widely distributed in D. molle tunicates and their predatory slug, P. forskalii. A) A molecular network of AEBA-containing metabolites from D. molle from the Solomon Islands. Nodes are colored according to type of compound identified. Compounds 1-5 (blue circles) are also found in P. forskalii. The size of the nodes is proportional to the number of tunicate specimens in which the compound was identified. B) Representative morphotypes of D. molle tunicates from the Solomon Islands, from which the compounds shown in panel A were identified. C) Distribution of AEBA-containing compounds shown in the network in panel A. The coloring scheme is identical to that used in panel A. Molleamine compounds (blue) were first identified in the P. forskalii specimen described here, and they are widespread in the slug’s tunicate prey. Other mollureas (pink) and mollecarbamates (yellow) are also found in many of the animals.