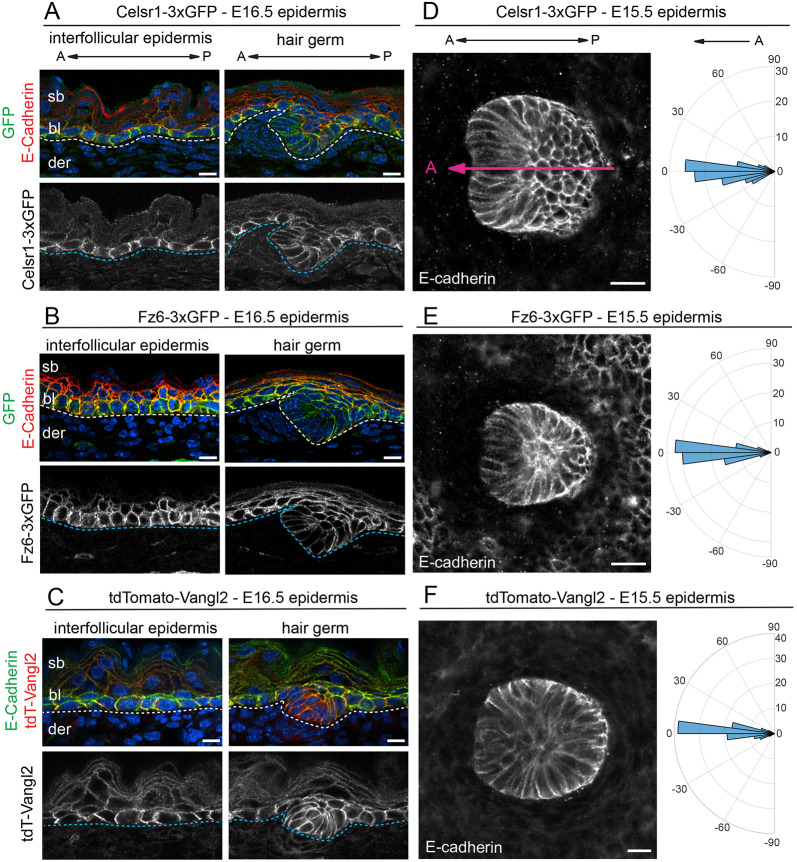
Fig. 2.
Expression and function of Celsr1-3xGFP, Fz6-3xGFP and tdTomato-Vangl2 in the embryonic skin. (A-C) Expression and localization of PCP fusion proteins in the interfollicular epidermis and developing hair follicles (HF) in E16.5 homozygous embryos. Sagittal cryosections were labeled with E-cadherin and Hoechst to mark nuclei (blue). (A) Celsr1-3xGFP (green), E-cadherin (red). (B) Fz6-3xGFP (green), E-cadherin (red). (C) tdTomato-Vangl2 (red), E-cadherin (green). Dotted lines indicate position of the epidermal-dermal boundary. Note that Celsr1-3xGFP, Fz6-3xGFP and tdTomato-Vangl2 are expressed primarily in the basal layer. (D-F) HF orientations at E15.5. Planar views of single HFs of flat-mount epidermis with E-cadherin are shown. Quantification of HF alignment is shown in circular histograms. Anterior is to the left (at 0°). Vectors point toward the anterior, growing end of HFs. (D) Celsr1-3xGFP, n=184, three embryos. Magenta line overlaid on the HF indicates orientation, where the anterior is marked by low E-cadherin expression. (E) Fz6-3xGFP homozygous, n=361, three embryos. (F) tdTomato-Vangl2 homozygotes with a curly tail and closed neural tube phenotype (CNT), n=434, three embryos. Note that in all three homozygous lines, HFs point anteriorly and align along the A-P axis, similar to their orientations in wild-type epidermis (Fig. S1). bl, basal layer; der, dermis; sb, suprabasal layer. Scale bars: 10 µm (A-C); 20 µm (D-F).