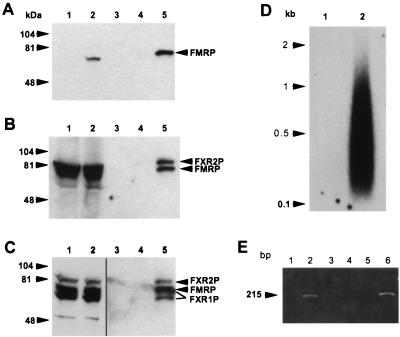
FIG. 2.
FXR1P and FXR2P assemble with Flag-FMRP in transfected L-M(TK−) cells to form an mRNP particle that binds mRNA. (A) Cytoplasmic lysates from approximately 5 × 105 L-M(TK−) cells expressing vector alone and expressing Flag-FMRP were loaded into lanes 1 and 2, respectively; lanes 3 to 5 contain Flag peptide elutions from the anti-Flag antibody M2 alone (lane 3) or from immunoprecipitations of 107 cells expressing the vector -only (lane 4) or Flag-FMRP (lane 5). The immunoprecipitated FMRP in lane 5 appears to run slower than the FMRP detected in the cytoplasmic lysates, probably because there is much less protein in the lanes containing the peptide elutions than in the lanes containing cytoplasmic lysates. The gel was blotted and sequentially probed with a monoclonal antibody recognizing FMRP (A), then with both anti-FMRP and anti-FXR2P antibodies (B), and finally with anti-FMRP, anti-FXR2P and anti-FXR1P antibodies (C). Lanes 1 and 2 in panel C are shown as separate because they are a lighter exposure of the same blot. Positions of the molecular weight standards are shown on the left, and positions of the proteins are shown on the right. The long and short isoforms of FXR1P are indicated by lines. (D) mRNA was purified from L-M(TK−) cells expressing either the vector only (lane 1) or Flag-FMRP (lane 2) as described in Materials and Methods. The mRNA was recovered, and the polyadenylated species were labeled by priming with oligo(dT) and synthesizing first-strand cDNA with reverse transcriptase. (E) MRNA obtained from immunoprecipitations of L-M(TK−) cells expressing either Flag-FMRP (lanes 1 and 2) or vector alone (lanes 3 and 4) or from mouse brain (lanes 5 and 6) was reverse transcribed with an oligo(dT) primer in either the presence (lanes 2, 4, and 6) or the absence (lanes 1, 3, and 5) of reverse transcriptase. A fraction of each reaction mixture was then added to a PCR mixture with mouse FMR1 primers. The PCR products were resolved on an agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide.