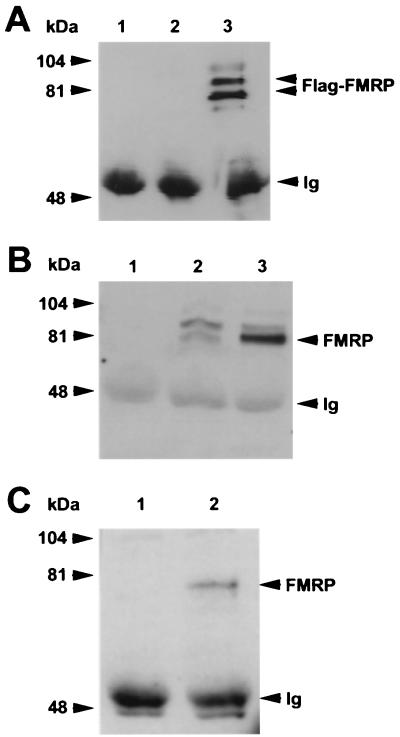
FIG. 5.
FMRP coimmunoprecipitates with nucleolin. (A) Lane 1 contains the antinucleolin antibody alone; lanes 2 and 3 show antinucleolin immunoprecipitation of cytoplasmic lysates from 107 L-M(TK−) cells expressing the vector alone and from 107 L-M(TK−) cells expressing Flag-FMRP, respectively. The proteins were resolved on a 7.5% gel, blotted to nitrocellulose, and probed with anti-Flag antibody M2. Positions of the molecular weight markers are shown on the left, and positions of FMRP and the heavy chain of the antinucleolin antibody (immunoglobulin [Ig]) are shown on the right. (B) An experiment similar to that shown in panel A except that transferred proteins were probed with the anti-FMRP antibody. Lanes 1 to 3 are as described above: the antinucleolin antibody alone, an immunoprecipitation of vector-only-containing L-M(TK−) cells, and an immunoprecipitation of Flag-FMRP-expressing L-M(TK−) cells with the antinucleolin antibody. In lane 2, the endogenous murine FMRP is immunoprecipitated with nucleolin in addition to the Flag-tagged FMRP observed in lane 3. Positions of the heavy chain of the antinucleolin antibody, which reacts with the second-step goat anti-mouse HRP conjugate, and Flag-FMRP are indicated on the right. (C) Total brain homogenates were prepared from either FMR1 knockout mice (lane 1) or their wild-type, FMRP-positive littermates (lane 2). The cytoplasmic lysates were immunoprecipitated with the antinucleolin antibody, washed extensively, and boiled. The samples were resolved on a 7.5% gel, transferred to nitrocellulose, and then probed with a monoclonal antibody that recognizes FMRP. Positions of FMRP and the heavy chain of the antinucleolin antibody are shown on the right.