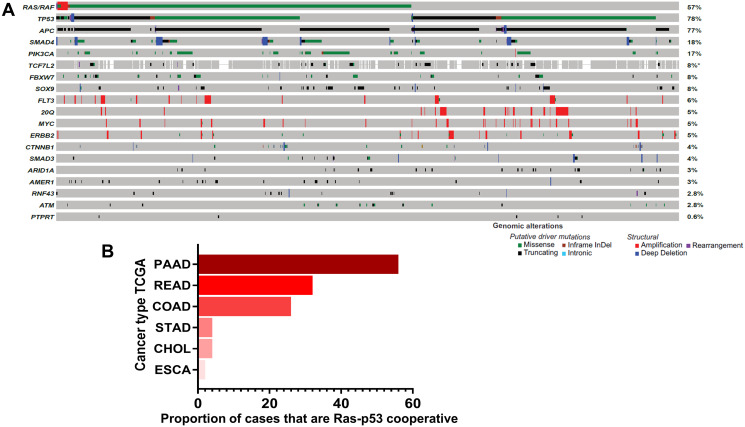
Figure 1. Ras-p53 genomic cooperativity in gastrointestinal cancer.
(A) Oncoprint demonstrating most frequent putative driver alterations in patients with colorectal cancer in the MSK-IMPACT Clinical Sequencing Cohort (available through http://www.cbioportal.org). Gene names are provided to the left and mutational frequencies to the right. Genomic alterations are classified as putative driver or structural alterations in adjoining legend. (B) Frequency of co-altered Ras pathway and p53 alterations were determined in patients with pancreatic cancer (PAAD), rectal cancer (READ), colon cancer (COAD), stomach cancer (STAD), cholangiocarcinoma (CHOL), and esophageal (ESCA) cancer in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset.