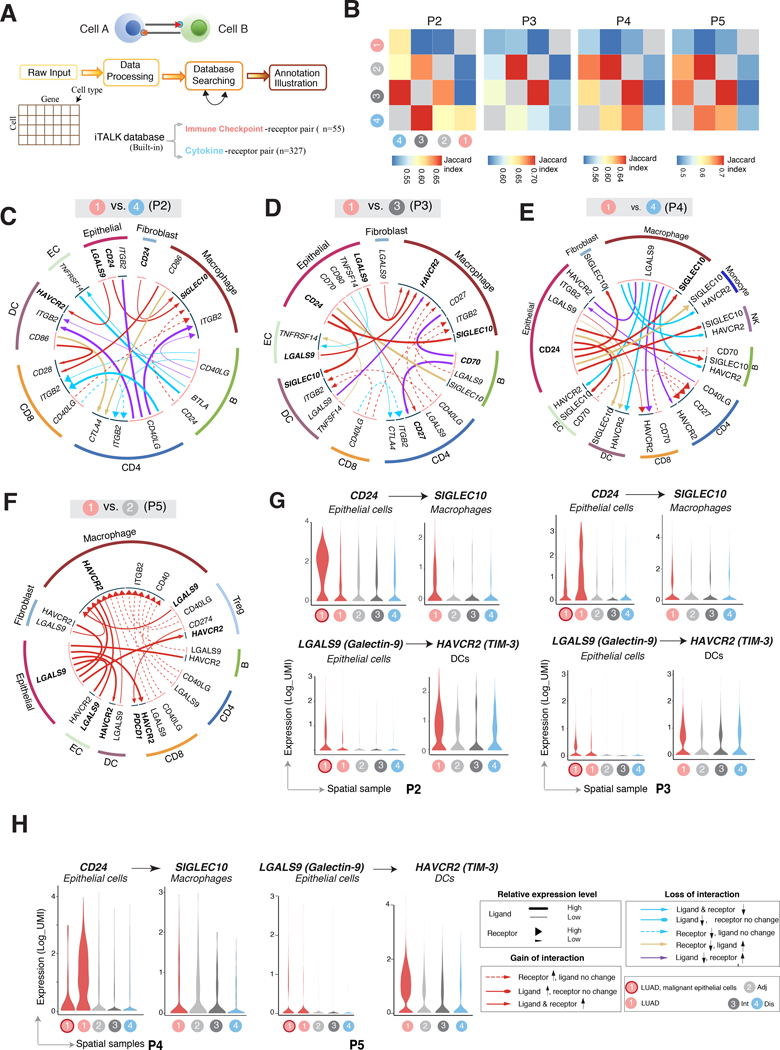
Figure 5. Enriched ligand-receptor cell-cell communication networks between LUADs and their immune microenvironment.
A, Computational analysis workflow of cell-cell communication using iTALK to identify, from a database of curated ligand-receptor (L-R) pairs, the highly expressed immune checkpoint- and cytokine-receptor pairs, that are significantly and differentially altered (i.e., interactions lost or gained) between LUADs and spatial normal lung tissues. B, Heatmaps showing the overlap (quantified by Jaccard index) of predicted ligand-receptor based interactions among individual LUADs and their corresponding spatially distributed normal lung tissues. C-F, Representative circos plots showing details of immune checkpoint-mediated L-R pairs compared between each of the LUADs of patients 2 (C), 3 (D), 4 (E) and 5 (F), and selected matching spatial normal lung samples. G-H, Violin plots showing expression of the ligand and receptor genes (selected from panels C-F) involving immune checkpoints and showing spatial gain-of-interaction patterns as highlighted in circus plots for patient 2 (panel G left), 3 (panel G right), 4 (panel H left) and 5 (panel H right).