Figure 3. Diverse roles of EZH2 in prostate cancer.
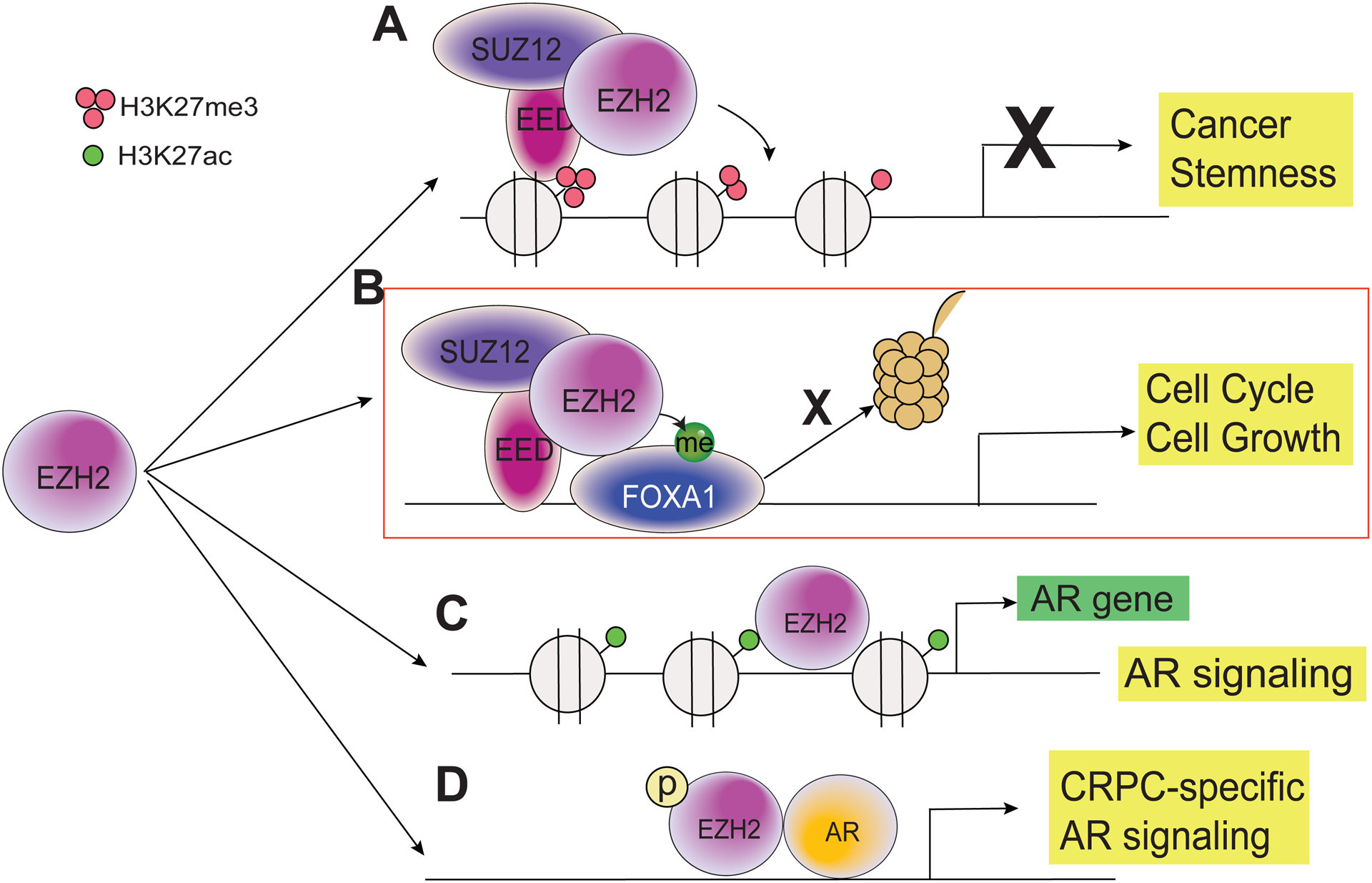
(A) The canonical function of EZH2 is to form the PRC2 complex with other core subunits SUZ12 and EED to catalyze H3K27me3, which leads to epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes, rendering cancer cell stemness. (B) FOXA1 is a non-histone substrate of EZH2 in prostate cancer. EZH2 methylates FOXA1 and protect it from protein degradation. EZH2 and FOXA1 co-regulates cell cycle progression and prostate cancer growth. (C) EZH2 directly binds at the AR gene promoter to induce AR gene transcription. This function is independent of PRC2 and EZH2 MTase activities. (D) In CRPC cell line LNCaP-abl, phosphorylated EZH2 has been shown to act as an AR co-activator to drive AR signaling and CRPC progression.
