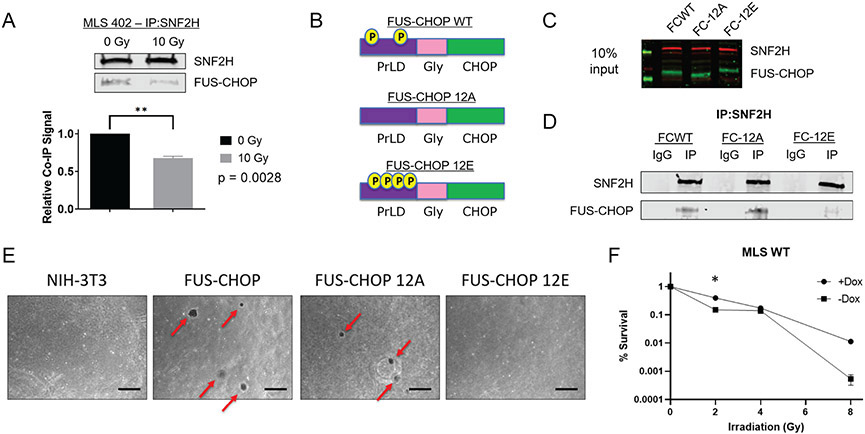
Fig. 4. Ionizing radiation decreases protein-protein interactions between SNF2H and FUS-CHOP by DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of the PrLD.
(A) Co-IP of SNF2H and FUS-CHOP 45 minutes after either sham or 10 Gy X-ray irradiation. ** p = 0.0028, unpaired t-test. (B) Schematic of FUS-CHOP wild type, phospho-dead (12A), and phospho-mimic (12E) cDNA constructs. (C) NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing FUS-CHOP and its phosphomutant forms. (D) Co-IP of SNF2H in NIH-3T3 cell lines stably expressing FUS-CHOP (FCWT), FUS-CHOP 12A (FC-12A), and FUS-CHOP 12E (FC-12E). (E) Soft agar colony formation assay to evaluate cellular transformation using NIH-3T3 cells that stably express either wild type FUS-CHOP or phosphomutant forms of FUS-CHOP. Representative images from two technical replicates are shown. Scale bars = 500 μm. (F) Clonogenic assay of human MLS 402 cells with and without dox-inducible shRNA targeting endogenous FUS-CHOP at 2, 4, and 8 Gy X-ray irradiation. *, p < 0.05