Figure 7. BT-GSI decreases tumor growth and reduces the progression of the osteolytic disease in immunodeficient mice with established human MM.
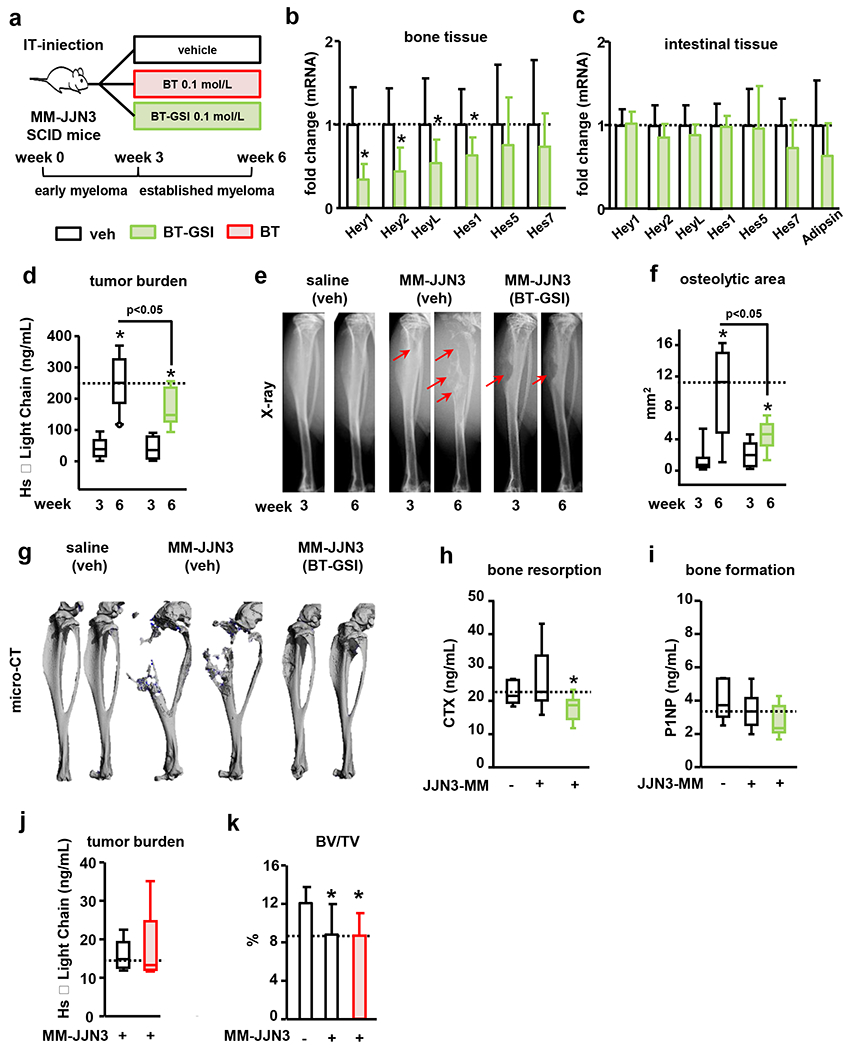
(a) Experimental design for BT-GSI and BT (105 JJN3 cells, IT-intratibial injection). Effects of BT-GSI (0.1mol/L, three times a week, 3 weeks) on (b-c) mRNA gene expression of Notch targets in bone and intestinal tissue, (d) serum human Kappa light chain, (e) tibia X-rays, (f) area of osteolytic lesions, (g) 3D microCT reconstruction images of PBS/MM cells injected tibias, (h) serum levels of CTX and (i) P1NP. Bars represent means ± SD. n=7-11/group. Effects of BT on serum human Kappa light chain 6 weeks after MM cell inoculation (j), and bone volume over tissue volume (BV/TV) in the cancellous bone of tibias inoculated with JJN3 MM cells (k). Bars represent means ± SD. n=9-10/group. *p<0.05 vs 3 weeks (d-f) or vs MM-veh (b, c, l). Red arrows indicate osteolytic lesions. Horizontal dotted lines indicate the mean value for vehicle-treated mice bearing MM tumors. Fold changes in mRNA expression were calculated by dividing the treatment values by the control/vehicle values.
