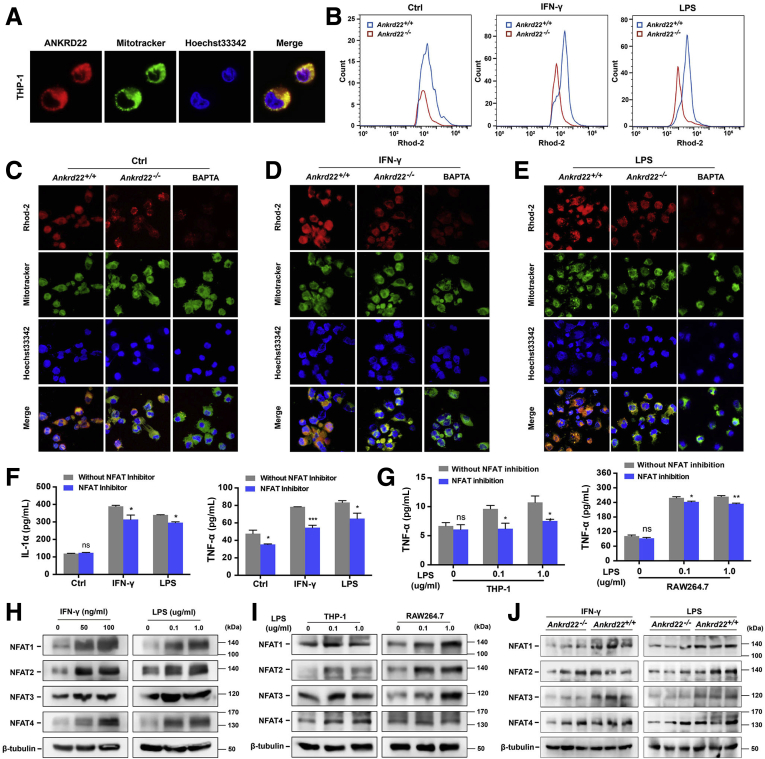
Figure 6.
ANKRD22 deletion reduces the expression levels of mitochondrial Ca2+and cytoplasmic NFAT in macrophages. (A) Mitochondrial colocalization of exogenous-expressing ANKRD22 in THP-1 macrophages detected by confocal microscopy. (B–E) Ankrd22 knockout reduced the mitochondrial Ca2+ level in activated mouse macrophages. Confocal microscopy was used to compare the fluorescence intensity and colocalization with mitochondria. Macrophages treated with 50 μmol/L 1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid (BAPTA) for 24 hours was used as a negative control. The fluorescence intensity was detected by Rhod-2–based FCM. (F) Determination of IL1α and TNF-α in supernatant of activated mouse macrophages by ELISA after NFAT inhibition. The activated macrophages were treated with 100 ng/mL NFAT inhibitor for 1 hour. (B–F) Macrophages were stimulated with 50 ng/mL IFN-γ or 100 ng/mL LPS or PBS (Ctrl) for 24 hours. (G) Determination of TNF-α in the supernatant of activated macrophages by ELISA after NFAT inhibition. The LPS-activated macrophages were treated with 100 ng/mL NFAT inhibitor for 1 hour. (H) Detection of NFAT in the activated mouse macrophages by Western blot. (I) Detection of NFAT in the activated macrophages by Western blot. (G–I) THP-1 macrophages were treated with 100 ng/mL phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate for 24 hours in advance. (J) Effects of Ankrd22 knockout on the expression levels of NFAT in activated mouse macrophages detected by Western blot. Macrophages were stimulated with 50 ng/mL IFN-γ or 100 ng/mL LPS for 24 hours. Macrophages were stimulated with 0, 50, or 100 ng/mL IFN-γ or 0, 0.1, or 1.0 μg/mL LPS for 24 hours. Data are presented as means ± SD and analyzed using the Student t test. ∗P < .05 and ∗∗P < .01.