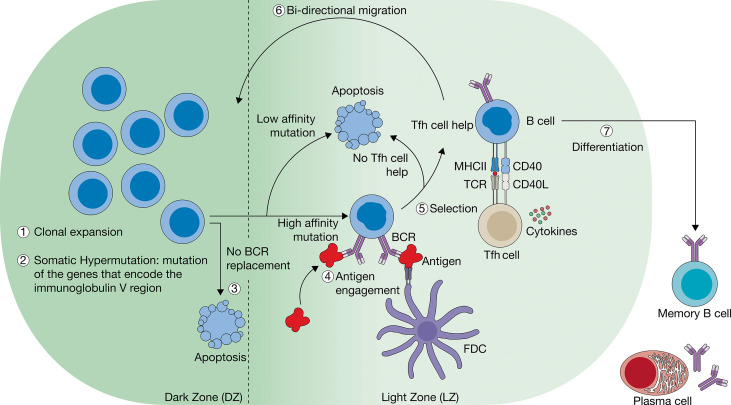
Figure 2.
The germinal center (GC) reactions. In the dark zone (DZ) of the GC, B cells undergo clonal expansion (1), which is accompanied by spontaneous point mutations in the gene that encodes for the variable domain of the B cell receptor (BCR) (2). GC B cells (GCBCs) with mutations that compromise BCR expression are removed through apoptosis (3). GCBCs with functional BCRs test the potentially altered affinity in the GC LZ through interactions with the antigen (4) and Tfh cells, which provide CD40L and cytokines (5). GCBCs that obtained a higher affinity BCR are expected to outcompete those with weaker affinity as a result of these interactions (4 and 5). Ultimately, positively selected B cells are the only ones to survive and either re-circulate to the DZ (6) or differentiate into either memory B cells (MBCs) or plasma cells (PCs) (7).