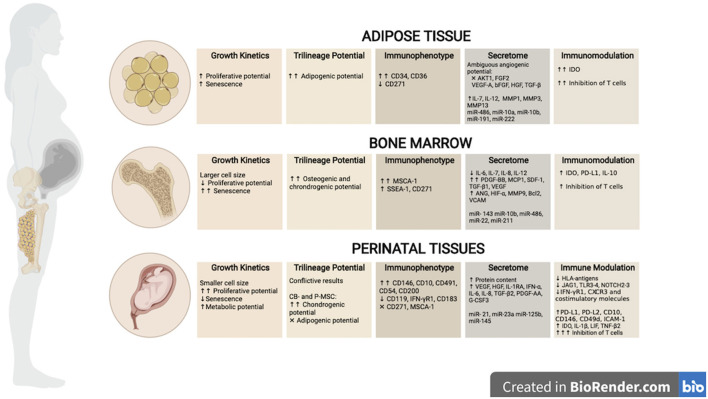
Figure 2.
Biological properties of tissue-derived MSCs. MSCs can be isolated from adult tissue sources such as adipose (AT)- and bone marrow (BM), as well as perinatal and/or birth-associated tissues, including amniotic liquid (AM), cord blood (CB), placenta (P) or umbilical cord (UC) tissues. Tissue of origin have shown to impact the biological properties of MSCs. This figure illustrates the main differences described in the literature regarding growth kinetics, differentiation abilities, immunophenotype, secretome, and immune modulation between cell sources. Created in BioRender.com.