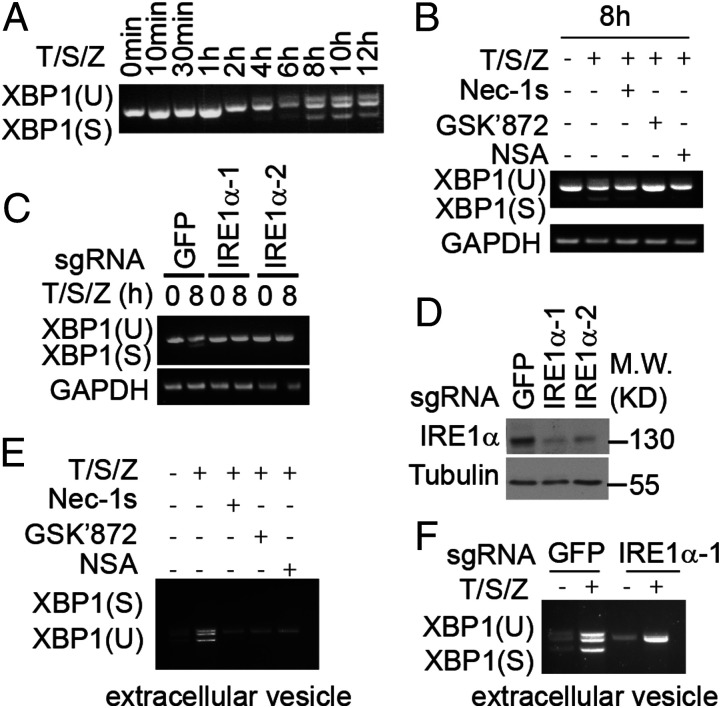
Fig. 4.
Incorporation of spliced XBP1 mRNA into extracellular vesicles during necroptosis. (A and B) HT-29 cells were treated with human TNF (50 ng/mL), SM-164 (100 nM), z-VAD.fmk (25 μM), Nec-1s (10 μM), GSK′872 (10 μM), and NSA (2.5 μM) as indicated. The cell lysate was collected and analyzed by RT-PCR. (C) Sg-GFP, sg-IRE1α-1, and sg-IRE1α-2 HT-29 cells were treated with human TNF (50 ng/mL), SM-164 (100 nM), and z-VAD.fmk (25 μM). The cell lysate was collected and analyzed by RT-PCR. (D) The knockout efficiency of sg-IRE1α-1, sg-IRE1α-2 HT-29 cells. (E) HT-29 cells were treated with human TNF (50 ng/mL), SM-164 (100 nM), z-VAD.fmk (25 μM), Nec-1s (10 μM), GSK′872 (10 μM), and NSA (2.5 μM) for 24 h. The exosome was isolated from culture medium and the RNA was analyzed by RT-PCR. (F) Sg-GFP, sg-IRE1α-1, and sg-IRE1α-2 HT-29 cells were treated with human TNF (50 ng/mL), SM-164 (100 nM), and z-VAD.fmk (25 μM) as indicated for 24 h. The exosome was isolated from culture medium and the RNA was analyzed by RT-PCR.