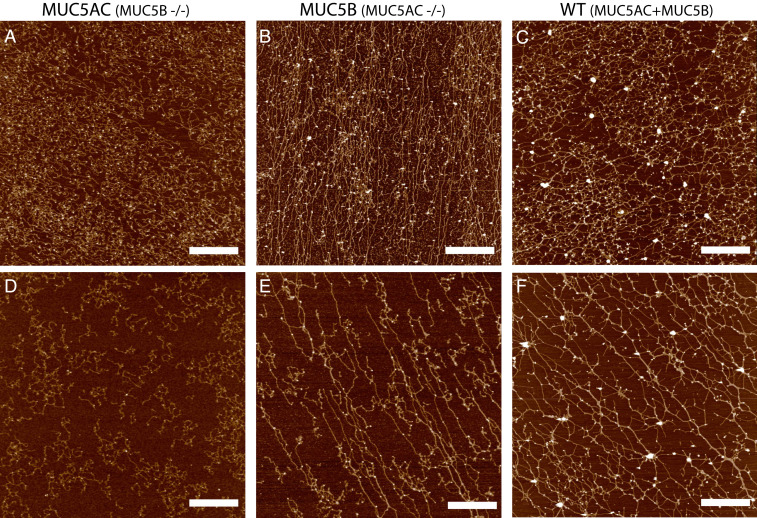
Fig. 2.
Isolated MUC5AC and MUC5B from monomucin cultures exhibit distinct macromolecular organization on surfaces. AFM images of mucins MUC5AC (A), MUC5B (B), and WT secretions (C) at a high concentration (∼100 μg/mL) and also imaged at a lower concentration ∼30 μg/mL (D–F). MUC5AC mucin polymers (A, D) form more compact structures with fewer (if any) long linear structures, while MUC5B (B, E) networks form polymers with a higher frequency of linear straight structures. WT Calu3 secretions (C, F), which contain both MUC5AC and MUC5B mucins at a 3:1 ratio exhibit a distinct mucin network that combines elements of both monomucin networks. (Scale bar, 1 μm.)