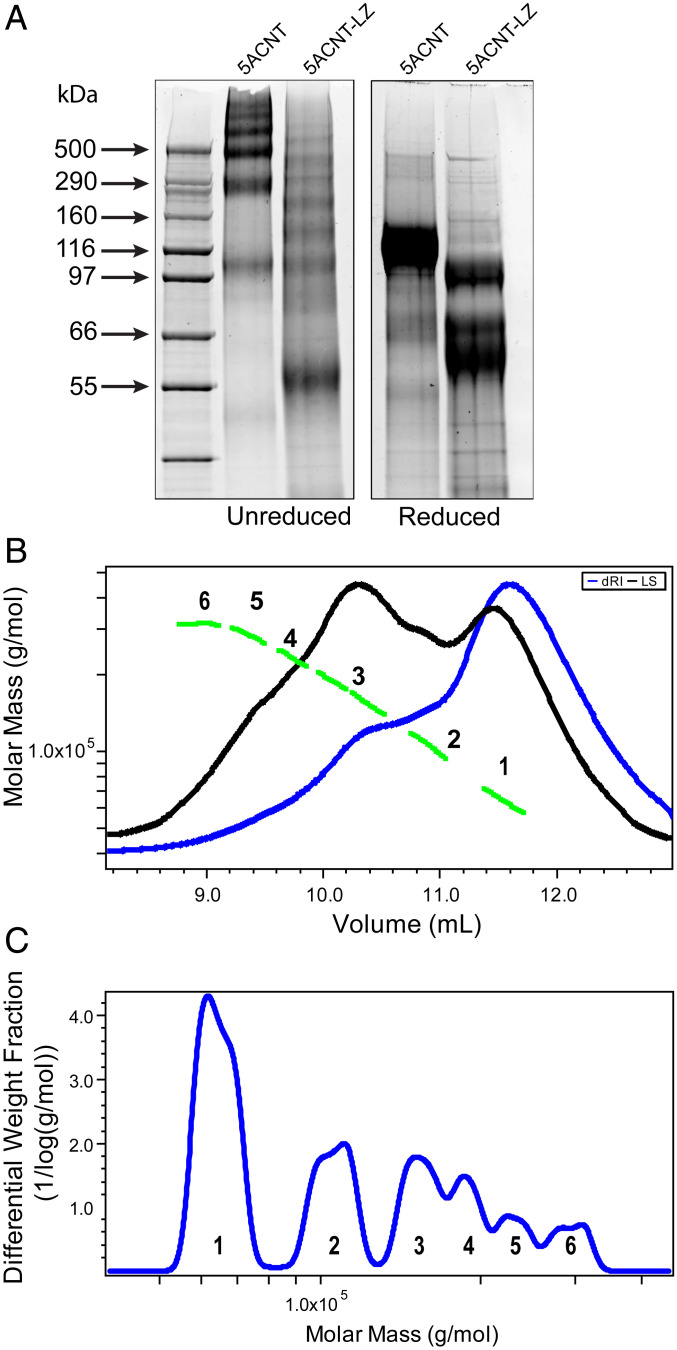
Fig. 6.
MUC5AC N-terminal domain with a mutated LZ (5ACNT-LZ) displays a different multimerization profile: (A) SYPRO Ruby staining of SDS-PAGE of purified protein products shows that 5ACNT-LZ maintains the ability to form higher-order oligomers, bands ranging from 55 to 500 kDa, despite no longer having the D3 domain present. For mass spectrometry analyses of the bands, see SI Appendix, Fig. S5. When reduced, the 5ACNT-LZ shows three monomeric bands, as compared to 5ACNT, which produced only one band after reduction. (B) SEC-MALLS analysis of the 5ACNT-LZ zipper–expressed protein shows traces of the purified 5ACNT-LZ protein on a Superose 6 column monitored by the tREX refractometer (blue) and Heleos II multiangle laser light scattering (black). The molar masses, obtained from MALLS, are shown across the 5ACNT-LZ distribution (green). (C) Molar mass distribution of 5ACNT-LZ multimers. Increasing molecular weight peaks are represented with numbers (1 to 6).