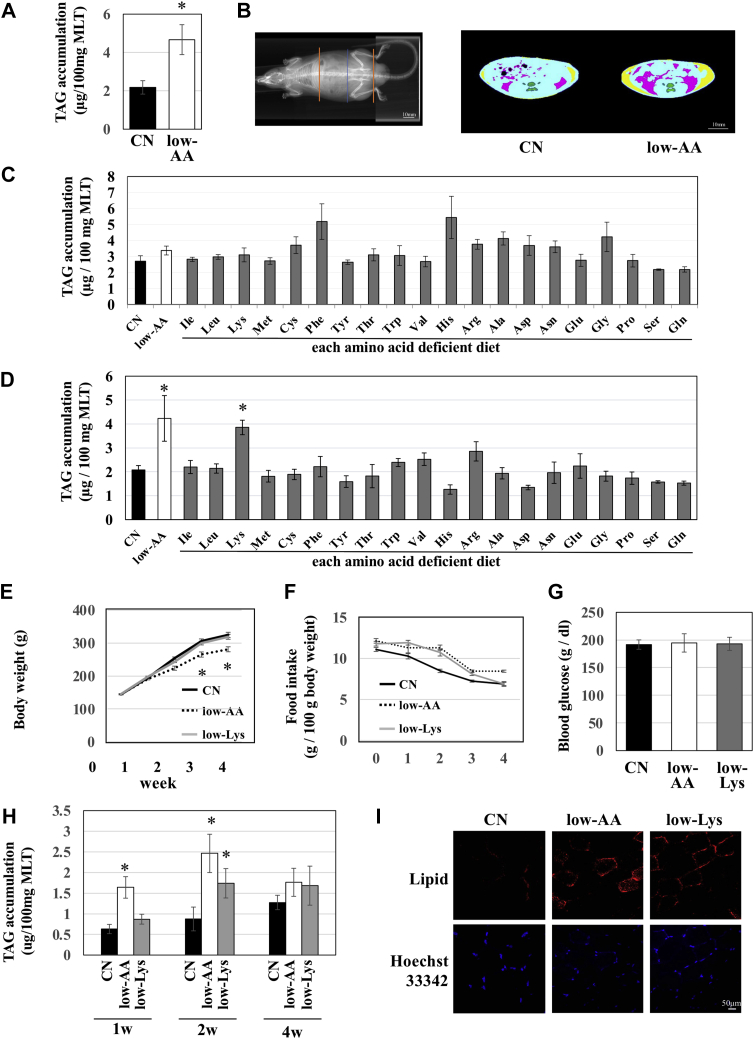
Figure 1.
Lipid accumulation in skeletal muscle of rats fed a low-AA or low-Lys diet. Six-week-old male Wistar rats were fed experimental diets ad libitum for 1 week (C), 2 weeks (A, B, and D–I), or 4 weeks (E, F, and H). A, C, D, and H, lipids were extracted from the skeletal muscles with methanol-chloroform solution according to Folch's method, and the TAG content was measured. The results are shown as μg TAG per 100 mg wet weight of MLT. n = 3, means ± S.E., ∗p < 0.01 versus CN. B, adipose tissue was measured using an X-ray CT scan. The ends of the scanned region are indicated by red lines, and the position of each representative CT scan image is indicated by the blue line (left panel). In the CT image, subcutaneous fat is shown in yellow, and visceral fat is shown in red (right panel). E and F, body weight and food intake were measured at 10 AM every day, and the values per 1 week are shown in the graph. n = 4, mean ± S.E. G, the blood glucose levels were measured and are shown in the graph. Lipids were stained with Lipid Tox and nucleus with Hoechst33342 in the frozen sections of MLT. Images were obtained using a confocal microscope.