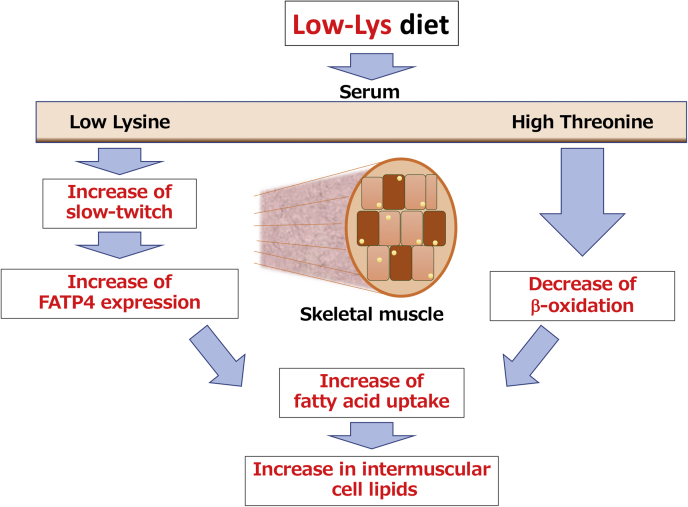
Figure 5.
Working hypothesis of a novel regulatory mechanism of the muscular lipid accumulation in rats fed a low-Lys diet. In the rats fed a low-Lys diet, the serum lysine levels are low while the serum threonine levels are high. Low levels of serum lysine may increase the ratio of slow-twitch muscle fibers, leading to increase in FATP4 expression. On the other hand, high serum threonine levels may inhibit β-oxidation via an unknown mechanism. These two changes in serum amino acid level are required for the increase in the fatty acid uptake, leading to intermuscular cell lipids.