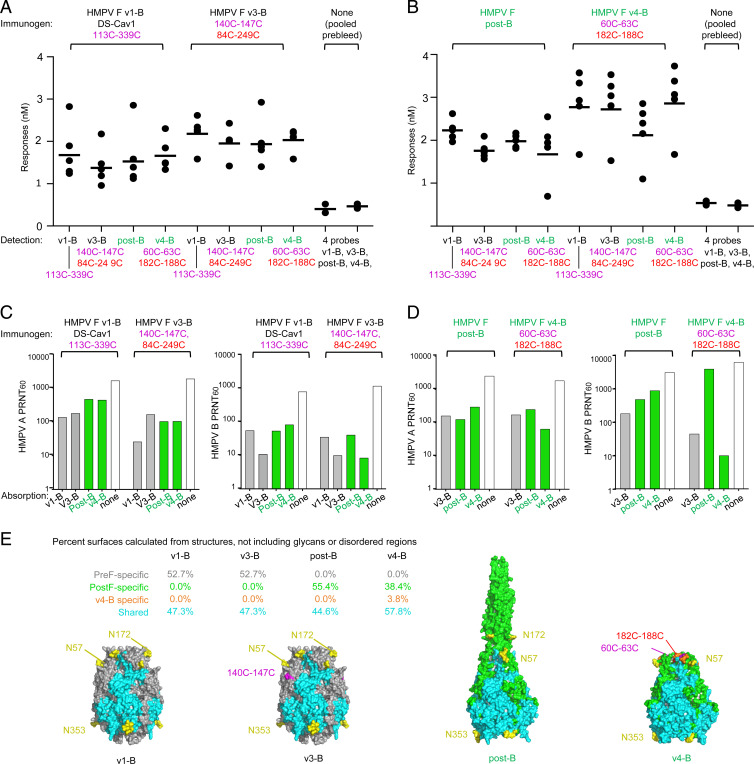
Fig. 5.
Serum analysis indicates neutralizing antibodies to mainly target epitopes shared between prefusion and interprotomer disulfide-stabilized postfusion HMPV F. Serum antibody binding analysis for rhesus macaques immunized with HMPV prefusion (A) and postfusion (B) F (post-B) or stabilized postfusion F v4-B (n = 5/group) using two prefusion HMPV F (black identifiers) and two postfusion HMPV F versions (green identifiers) as probes. (C and D) Neutralizing antibody responses for pooled rhesus serum (n = 5/group) of each group was absorbed with prefusion (v3-B), postfusion (post-B), and interprotomer disulfide-stabilized postfusion HMPV F (v4-B), respectively. (E) Immunogen shown with surfaces colored as being pre-F, post-F, or immunogen specific or shared between pre-F and post-F, with Inset providing % surfaces. Glycans N57 and N172 at the apex of the prefusion spike are likely shifting immune recognition away from this site, which is a prevalent site of neutralization in RSV.