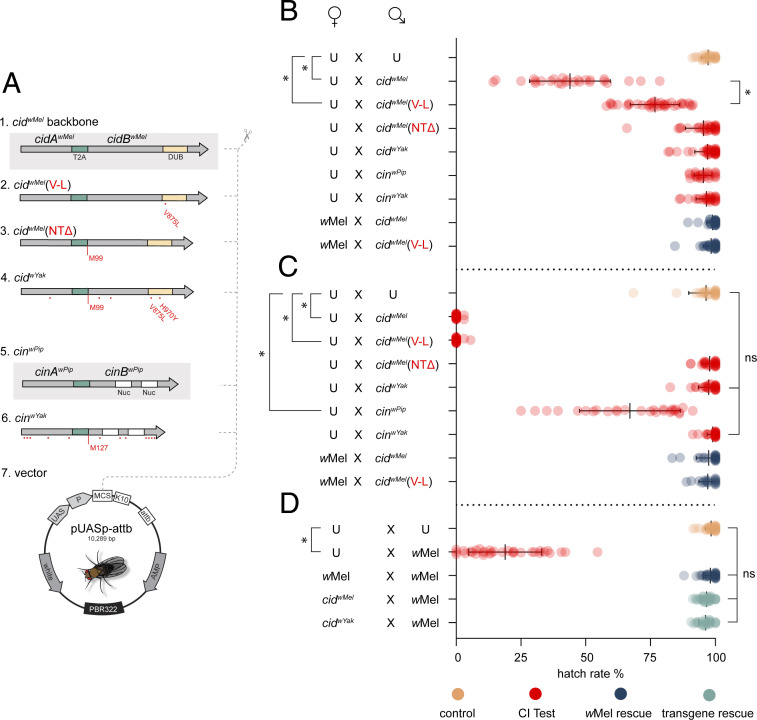
Fig. 2.
Analysis of mutations in a D. melanogaster model. (A) Design of transgene constructs. T2A is a viral sequence causing translation of two proteins. Red dots indicate amino acid changes. (M99) and (M127) label start codons after NTΔ. 1) positive CI control - the cidwMel backbone. 2) cidwMel (V-L) point mutant. 3) cidwMel (NTΔ) starting at M99. 4) cidwYak analog, in effect, wYak wild-type. 5) positive CI control, the cinwPip backbone. 6) cinwYak analog, in effect, wYak wild-type. 7) pUASp-attb insertion vector. (B) Transgenic CI with the weak NGT driver. Males expressing cidwMel cause strong CI relative to uninfected (U). Males expressing cidwMel(V-L) cause hypomorphic CI. wMel cytoplasmic infection rescues CI from males expressing cidwMel or cidwMel(V-L). (C) CI analysis with boosted expression using an MTD driver. Males expressing cidwMel or cidwMel(V-L) cause strong CI that cytoplasmic wMel infections in females fully rescue. Males expressing cinwPip cause weak CI. (D) Transgenic rescue. wMel cytoplasmic infection in males causes strong CI. wMel cytoplasmic infection in females rescues wMel-induced CI. Expression of operons cidwMel or cidwYak in females fully rescues wMel-induced CI. Raw hatch rates are plotted over means and SDs. (*) is P < 10−6, and (ns) is not significant. P values for B and C are calculated from one-tailed Wilcoxon tests with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons, while P values for D are calculated by a Kruskal–Wallis analysis with Dunn’s multiple comparison test.