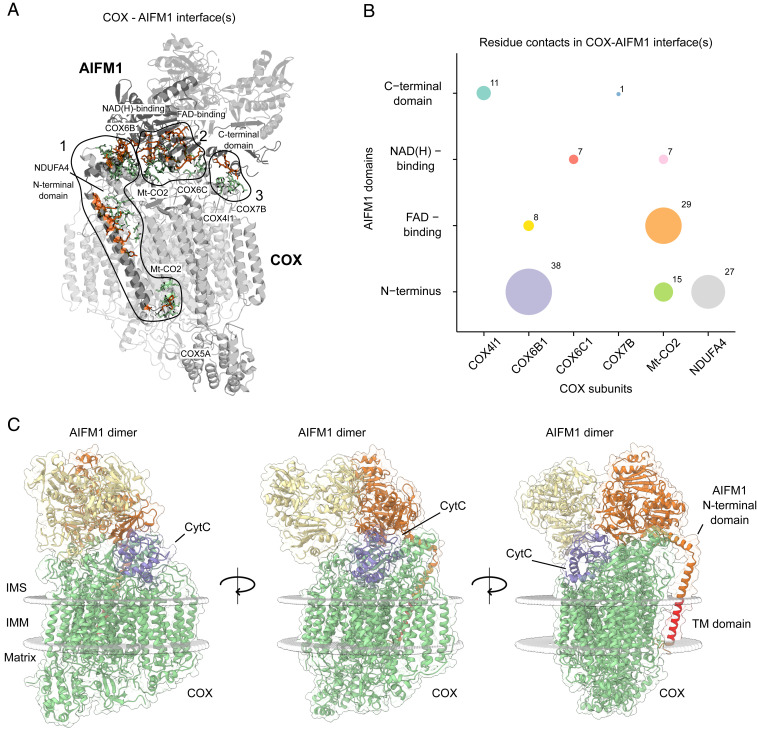
Fig. 4.
Deciphering interaction interfaces in the COX-AIFM12 structural model. (A) Three distinct interfaces between COX subunits and respective AIFM1 protomers were found. Subunits (COX) and protein domains (AIFM1) with residues in respective interfaces are colored in gray. Active COX residues are shown as green-colored sticks and active AIFM1 residues as orange-colored sticks. (B) Analysis of the number of residue contacts between respective COX subunits and AIFM1 domains. Colored circles indicate residue contacts between single subunits (COX) and domains (AIFM1) with the size of each circle corresponding to the number of residue–residue interactions. (C) COX-AIFM12 complex with CytC (purple) bound to its COX-binding site. The structural model presented here was merged with a previously published model of CytC docked to COX from bovine heart (54). COX subunits are colored green, while AIFM1 protomers are colored orange and yellow. The transmembrane (TM) domain of the N-terminal domain of AIFM1 is highlighted in red. Boundaries of the inner mitochondrial membrane are indicated as gray spheres.