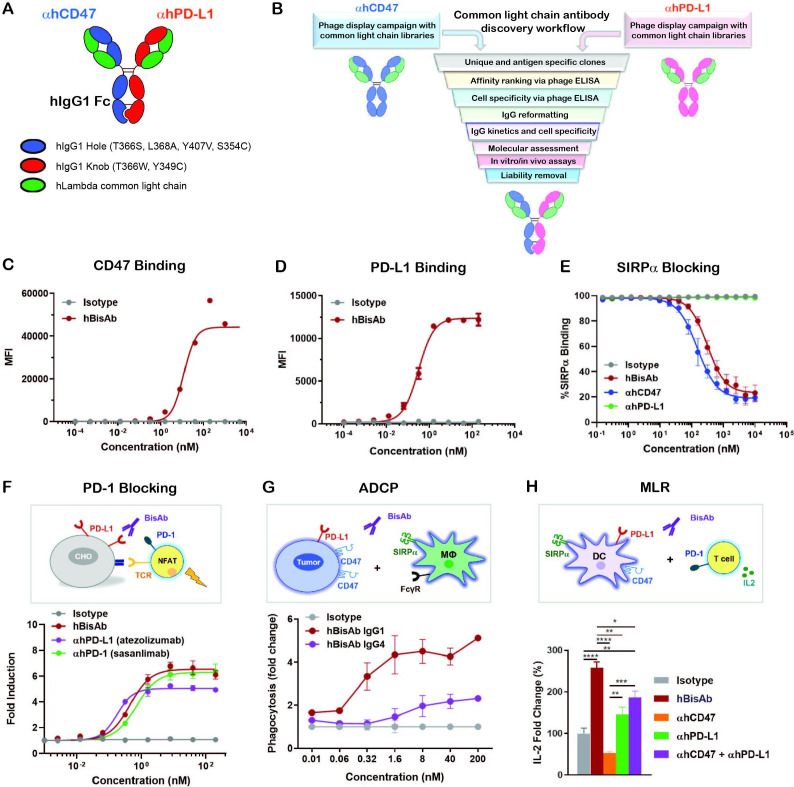
Figure 1.
Design and characterization of αCD47/PD-L1 bispecific antibody. (A) The schematic diagram of the human αCD47/PD-L1 bispecific antibody (hBisAb). (B) Workflow of common light chain antibody campaign for the generation of hBisAb. (C, D) Cell based binding of hBisAb on CHO-hCD47 (C), and CHO-hPD-L1 (D), as measured by flow cytometry. (E) In vitro blocking activity of hBisAb on the human CD47/SIRPα interaction as measured by flow cytometry. (F) In vitro blocking activity of hBisAb on the human PD-L1/PD-1 interaction using a PD-L1/PD-1 TCR blocking reporter bioassay. The blocking activity was quantified and normalized as the fold change compared with isotype control. (G) Phagocytosis of NCI-H292 human tumor cells by human monocyte-derived macrophages in the presence of human IgG isotype control, hBisAb in IgG1 or IgG4 format (n=2 donors/group). Phagocytosis of total tumor cells is represented as fold change compared with isotype treatment. (H) MLR assay was conducted to assess concentration of IL-2 at 72 hours in the supernatant by ELISA. A mixture of LPS matured DCs and purified CD4+ T cells were cocultured at a 1:4 ratio in the presence of αhCD47, αhPD-L1, the combination of αhCD47 and αhPD-L1, or hBisAb at 200 nM. *P<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA. ADCP, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; ANOVA, analysis of variance; DC, dendritic cell; IL-2, interleukin 2; MLR, mixed lymphocyte reaction; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TCR, T cell receptor.