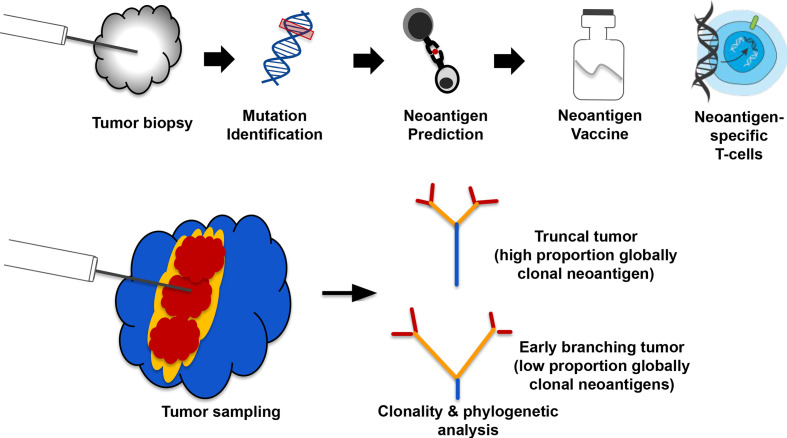
Figure 1.
An example of a neoantigen-specific immunotherapy (iNeST) workflow, and neoantigen heterogeneity analysis by multiregion sequencing. (A) Individualized iNeST targets neoantigens, which are unique to an individual’s tumor. A neoantigen vacccine is an example of an iNeST. (B) Mutational heterogeneity in metastatic disease settings may pose a problem for iNeST targeting and efficacy. Mutation/Neoantigen clonality varies across indications, with melanoma and non-small cell lung carcinoma having low heterogeneity (highly clonal), and colorectal adenocarcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, and breast cancer having high heterogeneity (low clonality). Predominantly primary tumors have been studied in non-metastatic disease setting, so the benefit of global mutation clonality prediction from standard clonality metrics determined using single tumor samples is unclear.