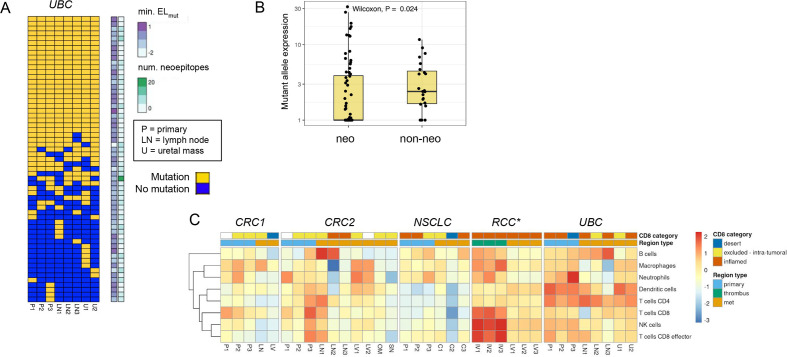
Figure 6.
Neoantigen expression loss and high immune inflammation across tumor regions in urothelial bladder carcinoma (UBC) case. (A) Sorted binary heatmap shows predicted neoantigens from the UBC case. There was no obvious relationship between neoantigen quality scores and neoantigen clonality/truncality. (B) In the UBC case, neoantigenic mutations (‘neo’) had reduced mutant allele expression relative to non-neoantigenic mutations (‘non-neo’). This trend was observed across all tumor regions, and was significant in 3/8 regions. (C) RNA expression signature analysis for immune cell types across tumor regions for each case. The CD8 immunohistochemistry (IHC) category is indicated at top, along with the type of tumor region. There was a consistent signature of inflammation across most UBC tumor samples related to dendritic cells and CD4 T cells. *Note that RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) failed for RCC primary samples, but the CD8 IHC phenotype for these regions was desert.