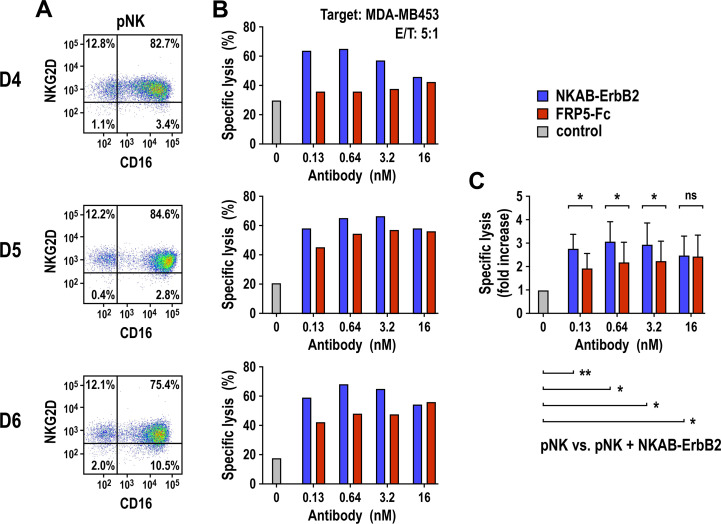
Figure 4.
Effect of NKAB-ErbB2 on the cell killing activity of donor-derived NK cells. (A) Expression of NKG2D and CD16 by the ex vivo expanded pNK cells from healthy donors (D4–D6, B) was analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-NKG2D and anti-CD16 antibodies as indicated. (B) Cytotoxicity of the pNK cells (A) against ErbB2-expressing MDA-MB453 breast carcinoma cells in the absence of bispecific antibody (gray bars) or in the presence of increasing concentrations of recombinant NKAB-ErbB2 (blue bars) or ErbB2-specific FRP5-Fc IgG1 mini-antibody (red bars) was investigated in flow cytometry-based cytotoxicity assays after coincubation at an E/T of 5:1 for 3 hours. (C) Normalized cytotoxicity data for pNK cells in the presence of NKAB-ErbB2 or FRP5-Fc (B) are plotted as fold increase in specific lysis in comparison to pNK alone. Mean values±SD are shown; n=3 individual donors. Data were analyzed by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. ns: p>0.05. E/T, effector to target ratio; NK, natural killer; NKG2D, natural killer group 2D; ns, not significant; pNK, peripheral blood NK.