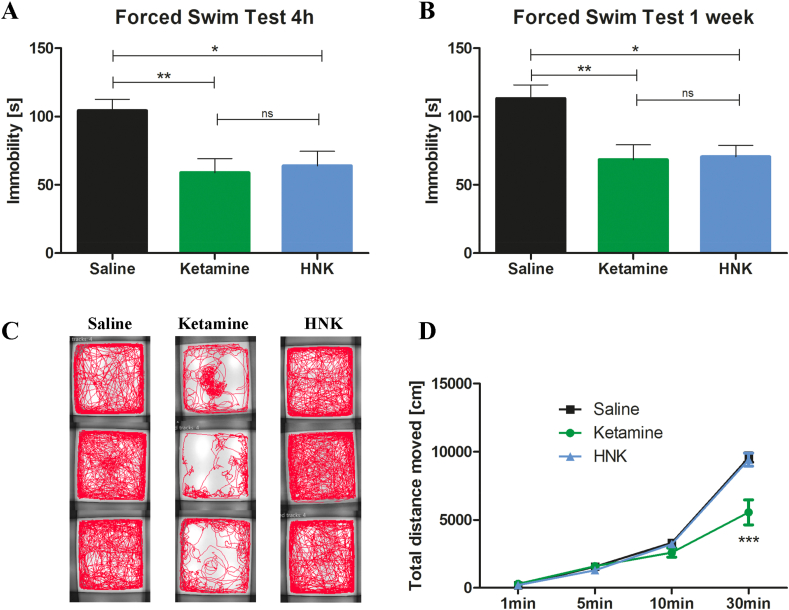
Fig. 1.
Antidepressant-like effects and side-effects of ketamine and HNK. (A) 4 h after injection, ketamine [t = 3.32, p < 0.01] and HNK [t = 2.96, p < 0.05] reduced immobility time in the FST [F = 7.44, p = 0.0019, n = 10 per group]. (B) 1 week after injection, ketamine [t = 3.24, p < 0.01] and HNK [t = 3.08, p < 0.05] reduced immobility time in the FST [F = 6.67, p = 0.0044, n = 10 per group]. (C + D) Ketamine affected locomotor activity [n = 10 per group]. (C) Ketamine-treated mice show an altered tracking profile [3 examples per group]. (D) Ketamine decreased locomotor activity [Interaction: F = 13.32, p < 0.001; time: F = 388.8, p < 0.001; treatment: F = 7.65, p < 0.01] compared to HNK [t = 7.79, p < 0.001] and saline [t = 8.10, p < 0.001] [n = 10 per group]. ns not statistically significant, HNK (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, bars are depicted as mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest in A + B, two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest in D.