Figure 1.
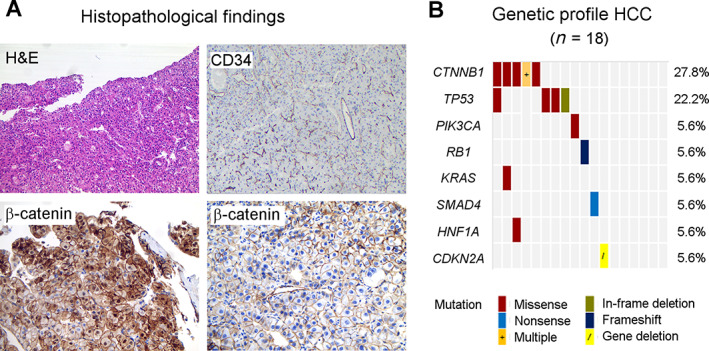
Tumor characteristics. (A): Representative HCC specimens, top panel: H&E and CD34 stains, respectively, show well differentiated HCC (×40 magnification) and typical high tumor vascular density (×25 magnification). Bottom panel from left to right: translocation of β‐catenin to the cytoplasm and nucleus in CTNNB1‐mutated HCC versus normal membrane β‐catenin expression in CTNNB1‐wildtype HCC (×100 magnification). (B): Molecular tumor profile by targeted next generation sequencing. Possible and known pathogenic gene mutations were most frequently found in CTNNB1 and TP53. CTNNB1 exon 3 variants: p.G34V, p.I35G38del, p.T41A, p.S45P, p.S45Y, and p.S45F mutations. TP53 exon 5 + 7 variants: p.T155K, p.C238R, p.G245C, and p.R249S mutations. Six tumors did not contain class 3–5 mutations in the evaluated genes or gene fragments. One patient with a CTNNB1 p.T41A and KRAS p.G12D mutation demonstrated aberrant nuclear β‐catenin staining at diagnosis, but wildtype CTNNB1 and membranous β‐catenin expression on the posttreatment sample. Abbreviation: HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.
