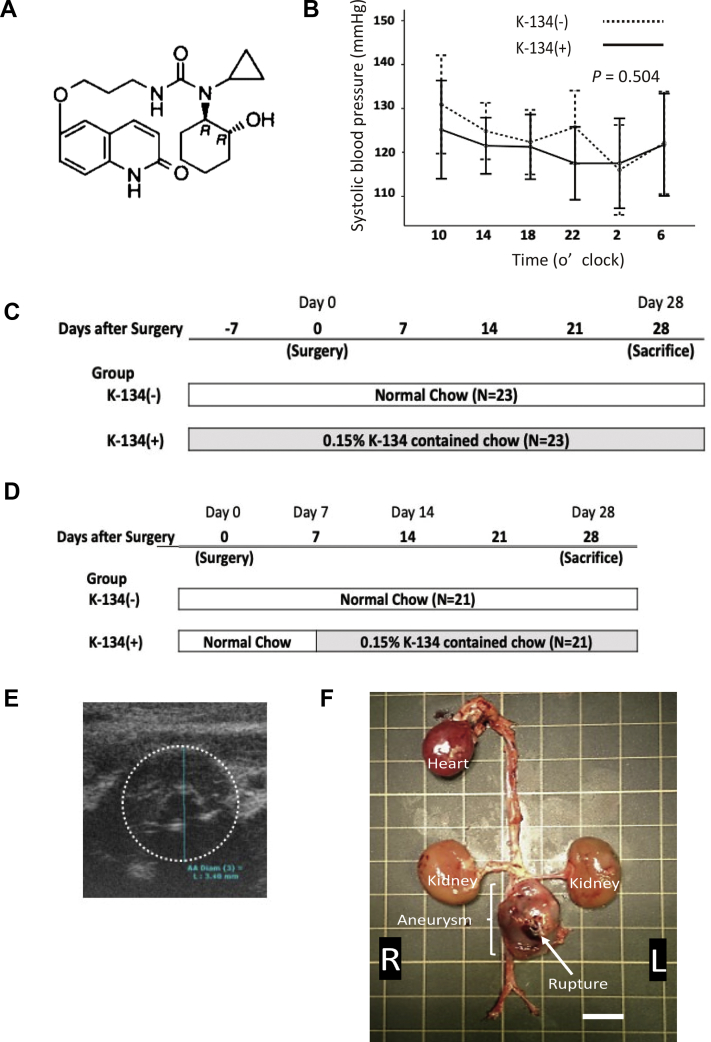
Fig 1.
Treatment protocol for hypoperfusion-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) rat model. A, Structural formula of K-134 (-)-6-(3-{3-Cyclopropyl-3-[(1R,2R)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]ureido}-propoxy)-2(1H)-quinolinone. B, Blood pressure measurement. Transition of systolic blood pressure (SBP) throughout the day with/without K-134 treatment (n = 5 per group). C, K-134 pretreatment protocol. The K-134(+) group (n = 23) was fed with a 0.15% K-134-containing diet, whereas the K-134(-) group (n = 23) was fed with a normal diet. The administration of K-134 started 7 days before the surgery (day 0), and both groups were observed for 28 days after day 0. D, Delayed K-134 treatment protocol. Rats were fed with a normal diet for 7 days after surgery. At day 7, rats with AAA >3.0 mm in diameter identified using ultrasound examination (E) were chosen and randomly divided into two groups: the K-134(+) group, which was fed with a 0.15% K-134-containing diet (n = 21), and the K-134(-) group, which was fed with a normal diet (n = 21). Both groups were observed for 28 days after day 0. F, Representative images of ruptured aneurysm, with the arrow indicating the rupture site, from rats without K-134 treatment. Scale bar = 10 mm.