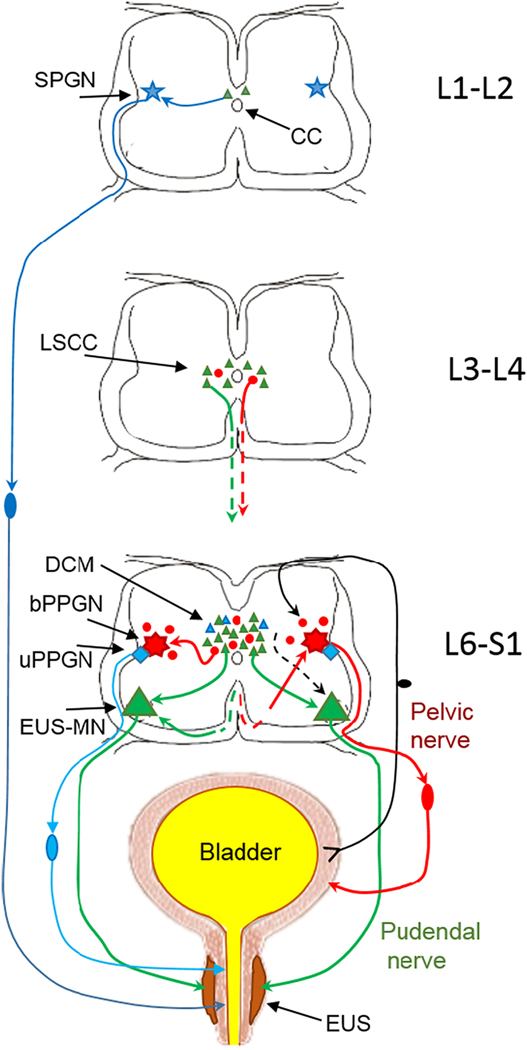
Fig.1.
Schematic of innervation of the lower urinary tract from lumbo-sacral segments of the spinal cord (connections with supralumbar structures are not included). External urethral sphincter (EUS) surrounding the smooth muscle of urethra is depicted in dark brown and the smooth muscle is in light brown. The striated muscle of the EUS receives excitatory input from motoneurons in Onuf’s nucleus in L6-S1 (EUS-MNs, large green triangles). In turn, EUS-MNs receive monosynaptic inputs from intrasegmental neurons located in L6-S1 dorsal commissure (DCM) and from intersegmental propriospinal neurons located in L3-L4 lumbar spinal coordinating center (LSCC) (small green triangles). The smooth muscle of urethra is activated by sympathetic preganglionic neurons (SPGN, blue star) in L1-L2. Parasympathetic input to urethral smooth muscle arises in preganglionic neurons (uPPGN, blue rhomboid)) in the L6-S1 IML. Both sympathetic and parasympathetic output neurons for the urethra smooth muscle have sets of local presynaptic interneurons near the central canal (small blue triangles). Since the EUS in rats and mice is only a couple of hundred microns thick in males and even thinner in females, an injection of PRV into EUS is always a challenge because often the smooth muscle is also partially infected. Therefore, after injection of PRV in the EUS, retrograde trans-synaptic tracing often results in some labeled cells in the upper lumbar segments (Vizzard, et al., 1995) which is also seen in Fig.2. Afferents from the bladder wall arrive to the dorsal horn of L6-S1 where they deliver information to parasympathetic preganglionic neurons (bPPGNs, red septagram) through a set of local interneurons (Araki, 1994;Araki and De Groat, 1996;Araki et al., 1997). bPPGNs like EUS-MNs receive inputs from local interneurons in the L6-S1 DCM and IML (small red circles) (Nadelhaft and Vera, 1996;Nadelhaft et al., 1992;Sugaya, et al., 1997) and from propriospinal neurons in L3-L4 LSCC (Karnup and De Groat, 2020b), i.e. from the area surrounding the central canal.