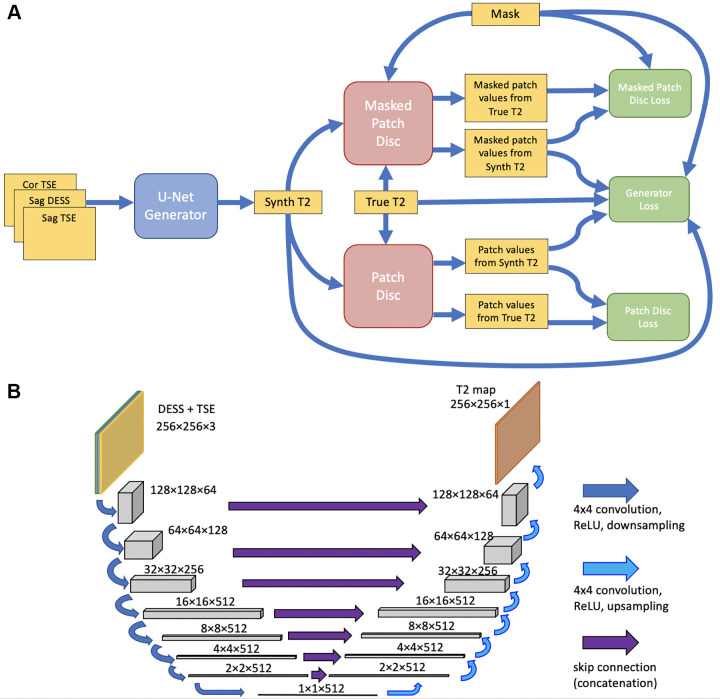
Figure 2:
(A) Schematic architecture of the neural network. A U-Net–based generator (blue) synthesizes a T2 map estimate from three anatomic scans. Patch-based discriminators (red) compare the synthesized (Synth) map to a true T2 map corresponding to the same anatomy. Loss functions (green), consisting of a combination of sigmoid cross-entropy and L1 loss, were computed and used to update the generator and the two discriminators. (B) Schematic illustration of the U-Net, taking the double-echo in steady-state (DESS) and turbo spin-echo (TSE) scans as input and producing an estimated T2 map as output. Cor = coronal, ReLU = rectified linear unit, Sag = sagittal.