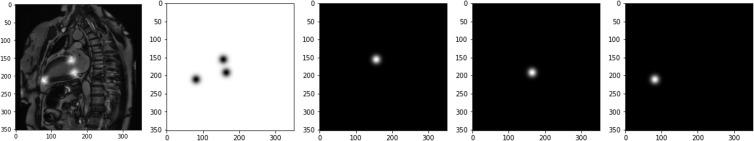
Figure 2:
The landmark detection problem can be reformulated as a semantic segmentation problem. Every landmark point on the two-chamber image on the left can be convolved with a Gaussian kernel and converted into a spatial probability map or heatmap (upper row, from left to right: probability for background, anterior valve point, inferior valve point, and apical point). Unlike in the binary detection task in which the target is a one-hot binary mask, loss functions working on continuous probability such as the Kullback-Leibler divergence are needed.