Fig 8. Zeb1 overexpression leads to extramedullary hematopoiesis/splenomegaly, enhanced myeloid cell development, and monocyte lineage skewing.
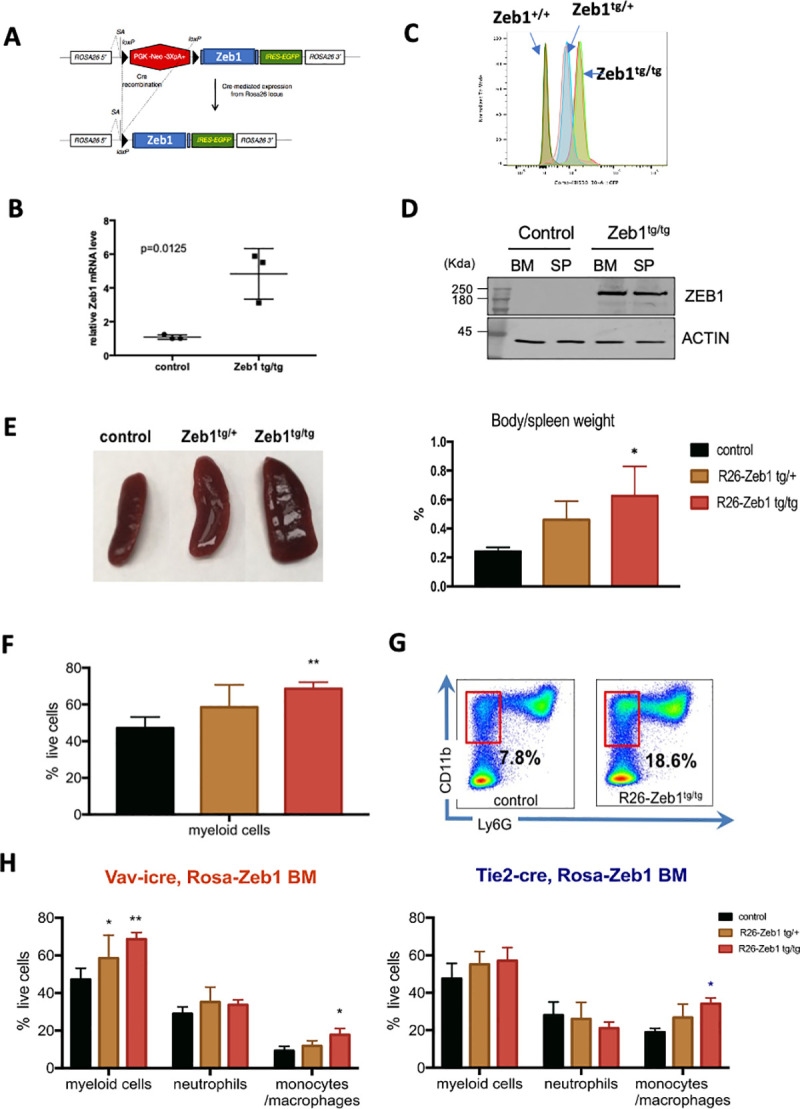
(A) Schematic of conditional Rosa26-Zeb1-IRES-EGFP-pA+ transgenic locus (left). (B) Following Vav-iCre-mediated deletion of the loxP flanked transcriptional stop cassette Zeb1 expression is increased approximately 4.5-fold in transgenic BM HSPCs compared to controls (N = three 5-month-old female mice/genotype, p = 0.0125; error bars indicate SD of the mean, Mann–Whitney test) along with (C) dosage-dependent EGFP expression in both heterozygous and homozygous Zeb1 transgenic HSPCs (Flow cytometry for EGFP). (D) Western blot confirmation of increased ZEB1 protein in the BM and spleen of Vav-iCre; Zeb1tg/tg mice compared to Cre-negative control samples. (E) Increased spleen size/extramedullary hematopoiesis seen in Zeb1tg/tg transgenic mice (left panel) showing roughly doubling in size compared to body weight (right panel). (F) Flow cytometric analysis showing increased myeloid cells in spleen (CD11b+, Gr1+). (G) Representative flow cytometry plot showing increased CD11b+, Lys6G- monocytes in the BM of Zeb1tg/tg mice. (H) Increases in myeloid cells (CD11b+, Gr1+) with monocytic skewing/expansion was present in both Vav-iCre (left) and Tie2-Cre models (right). Data are represented as mean + SD from 3 biological replicates/genotype. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, nonparametric t test. Raw data behind graphs and western blot in (D) are included in E of S1 and S2 Data, respectively. BM, bone marrow; HSPC, hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell; SP, spleen.
