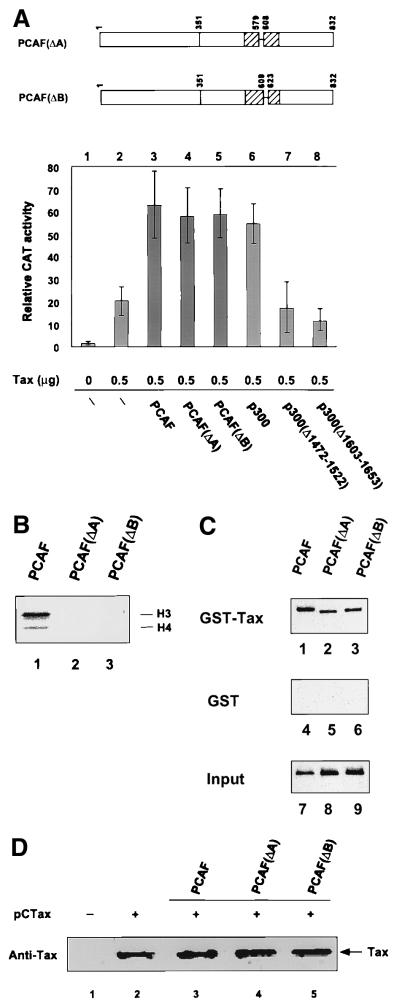
FIG. 7.
Effect of the PCAF HAT domain on HTLV-1 transcription. (A) Jurkat cells were transfected Tax and PCAF, PCAF HAT mutants, p300, or p300 HAT mutants as indicated, and CAT assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. PCAF(ΔA) contains a deletion of amino acids 579 to 608; PCAF(ΔB) contains a deletion of amino acids 609 to 623. Both deletion mutants lack HAT activity. Two p300 mutants containing deletions with the p300 HAT domain, amino acids 1472 to 1522 and 1603 to 1653, were compared to wild-type p300. The PCAF and p300 proteins were expressed from the same pCI vector. (B) Histone acetylation assay. Both PCAF(ΔA) and PCAF(ΔB) were expressed as Flag-tagged fusion proteins in baculovirus-infected cells and purified through an anti-Flag affinity column. The positions of histones H3 and H4 in the gel are indicated. (C) Interaction of GST-Tax with PCAF and PCAF deletion mutants. The GST binding assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. GST-bound proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE, and Western blot analysis was performed with an anti-Flag M2 antibody. The top, middle, and bottom panels represent GST-Tax-bound, GST-bound, and input PCAF protein, respectively. The bottom panel represents one-fourth of the PCAF added to the GST-Tax or GST binding assays. (D) PCAF, PCAF(ΔA), and PCAF(ΔB) do not increase Tax expression level. Jurkat cells were cotransfected with 5 μg of pCTax with either control plasmid (lane 2), PCAF (lane 3), PCAF(ΔA) (lane 4), or PCAF(ΔB) (lane 5). Nuclear extracts were made, and 60-μg aliquots of the proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE and analyzed by anti-Tax Western blotting.