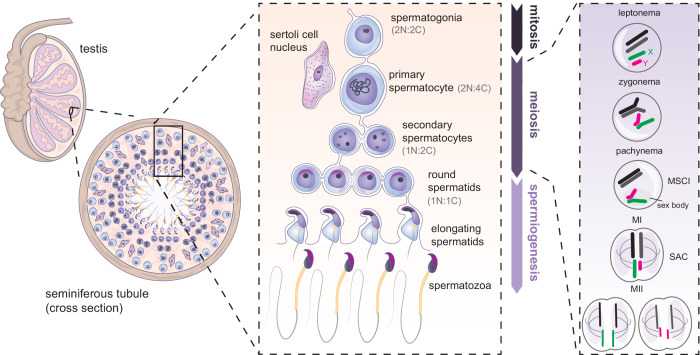
Figure 3. Mammalian spermatogenesis in seminiferous tubules of the testis.
Spermatogenesis occurs in three main phases: mitosis, meiosis and spermiogenesis. First, undifferentiated spermatogonial cells undergo multiple mitotic divisions. Subsequently, germ cells commit to meiosis, undergoing meiotic DNA replication (becoming 2 N:4 C) synapsis and recombination between homologues (shown in black and dark gray), and silencing of the X (green) and Y (magenta) chromosomes. Spermatocytes then undergo two rounds of cell division (becoming 1N:1C). The resulting round spermatids later undergo spermiogenesis, further specialising into mature spermatozoa. N = number of chromosomes, C = number of chromatids. SAC: spindle assembly checkpoint.