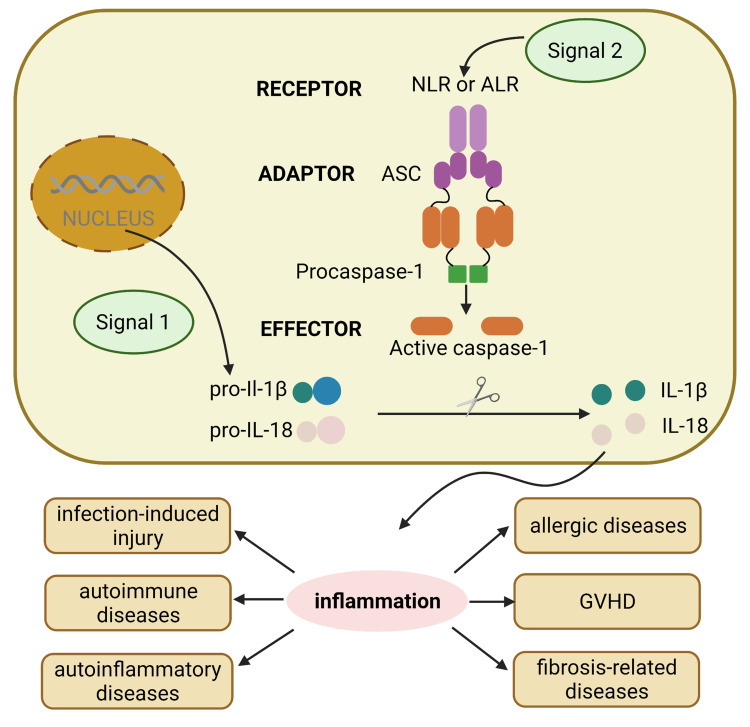
Figure 1.
The general process of activation of different inflammasomes. The assembly and function of inflammasomes involves two different steps: signal 1 including various PAMPs and DAMPs turns on the first initiation step, which upregulates the expression levels of inflammasomes components such as pro-IL-1β, pro-IL-18. Then, signal 2 triggers the second activation step, which induces oligomerization of the inflammasome complex including receptor NLRs and ALRs, adaptor ASC, and effector pro-caspase-1, the assembled pro-caspase-1 becomes caspase-1, then cutting pro-IL to activated IL, inducing inflammation response, which plays vital role in inflammation-related diseases including infection-induced injury, autoimmune diseases, autoinflammatory diseases, allergic diseases, GVHD and fibrosis-related diseases.
Abbreviations: PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPs, damage associated molecular patterns; IL, interleukin; NLRs, NOD-like receptors; ALRs, absent in melanoma 2-like receptors; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing caspase recruitment domain; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease.