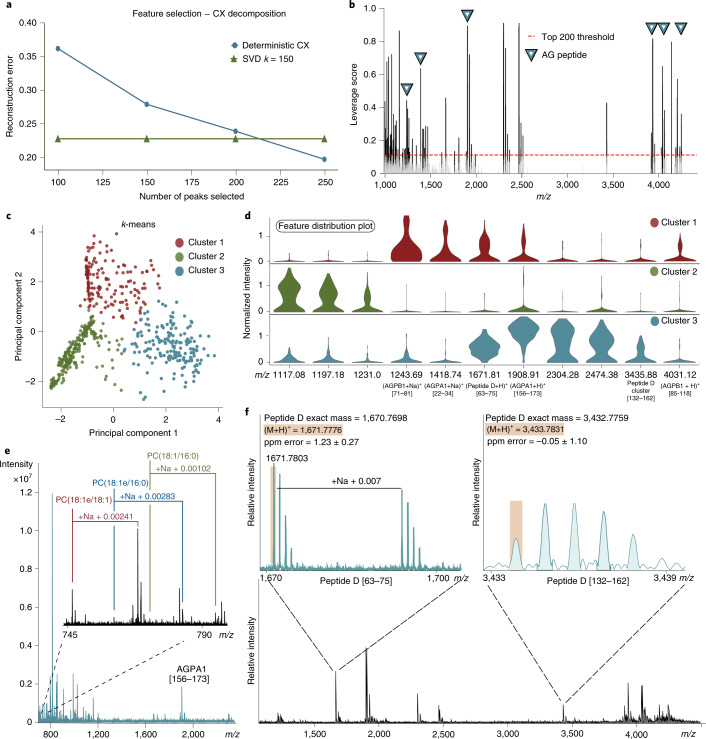
Fig. 2. Chemical heterogeneity of DCV populations: unsupervised data analysis, simultaneous acquisition of analyte classes and detection of novel Peptide D.
a, Deterministic CX was used to select 200 mass spectral features to improve data interpretation. CX decomposition was applied for feature selection where the best low-rank approximation was provided through singular value decomposition with a rank parameter k = 150, which was determined by the reconstruction errors with different rank parameters. Rank k = 150 has a reconstruction error less than 25% of the original dataset. b, ‘Statistical leverage scores’ for all spectral features were computed and plotted against the m/z axis. Multiple detected AG peptides can be seen with high leverage scores and are annotated with blue triangles. The ‘Statistical leverage score’ for each feature indicates its influence on the best low-rank fit of the data matrix. Selecting the top 200 features ensured that CX decomposition closely approximated the best low-rank fit of the original data matrix while removing uninformative information. c, Results of k-means clustering of the dataset containing 200 selected features with the highest statistical leverage score. d, Violin plots visualizing a subset of the selected features and their relative distribution in each cluster, with known AG peptides marked. e, Simultaneous detection of PC(18:1/16:0), PC(18:1e/16:0) and PC(18:1e/18:1) with their corresponding sodiated adducts annotated. f, The novel prohormone, Peptide D, was identified by MALDI MS mass-match assignment of Peptide D [63–75] and Peptide D [132–162]. SVD, singular value decomposition.