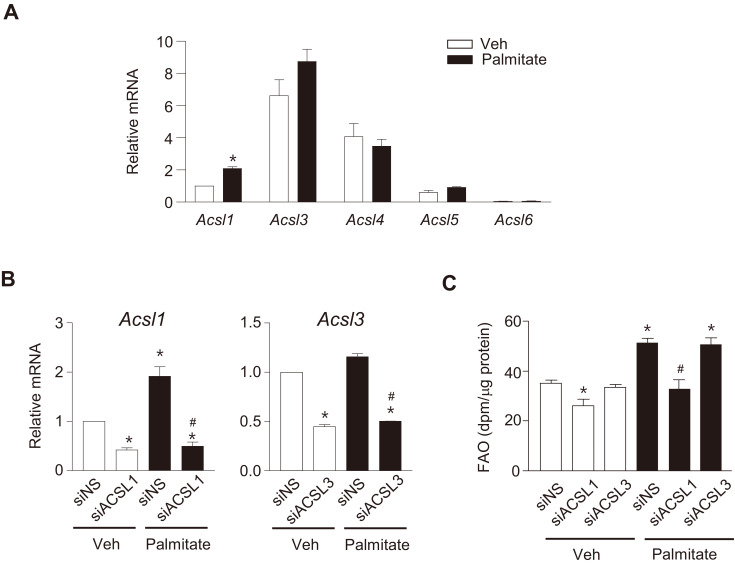
Fig. 4. ACSL1 mainly contributes to palmitate-induced FAO.
(A) C2C12 myotubes were treated with 500 μmol/L palmitate for 24 h and relative mRNA levels of ACSL isoforms were determined using qPCR. The ACSL1 mRNA level of untreated cells (Veh) was set to 1, and others were expressed as its relative values. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM, n = 3, *P < 0.05 vs Veh, by t-test. (B and C) C2C12 myotubes were transfected with siRNAs against ACSL1 and ACSL3 or siNS for 24 h and then treated with palmitate for 24 h. The mRNA levels of ACSLs (B) and FAO (C) were then determined. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 3, *P < 0.05 vs siNS/Veh, # P < 0.05 vs siNS/Palmitate, by ANOVA.