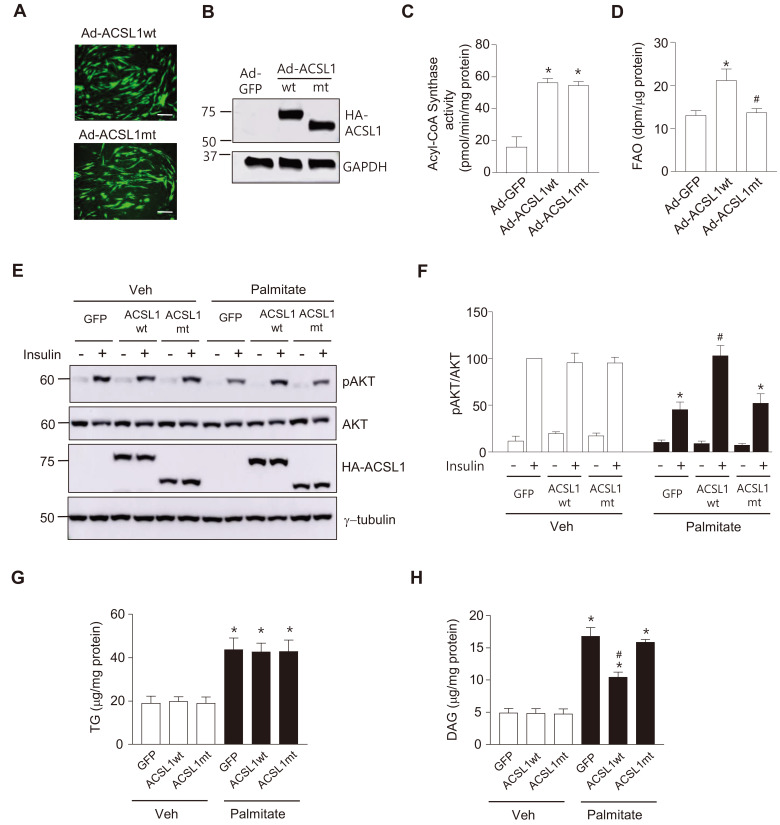
Fig. 5. ACSL1 overexpression ameliorates palmitate-induced insulin resistance.
(A-D) Acyl CoA Synthase activity and FAO were measured after myotubes were infected with Ad-HA-ACSL1wt, Ad-HA-ACSL1mt or Ad-GFP (control) (100 moi) for 24 h. Viral infection was compared by detecting green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression, Scale bars = 100 μm (A), and expression of HA-ACSL1wt and HA-ACSL1mt was confirmed by western blotting (B). (C) Acyl-CoA synthase activity was measured, and H2O2 production rates were normalized by the amount of proteins in the cell lysates. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 3, *P < 0.05 vs Ad-GFP, by ANOVA. (D) FAO rates were measured. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 4, *P < 0.05 vs Ad-GFP, # P < 0.05 vs Ad-ACSL1wt, by ANOVA. (E and F) C2C12 myotubes were infected with Ad-HA-ACSL1wt, Ad-HA-ACSL1mt, or Ad-GFP (100 moi) for 24 h followed by palmitate (250 μmol/L) treatment for another 24 h, then stimulated with or without insulin (100 nmol/L) for 30 min. (E) Western blot analyses were performed with specific antibodies against pAKT (Ser473), AKT, HA, or γ-tubulin. (F) The ratio of pAKT to total AKT in the western blots was measured. The value of insulin stimulated pAKT/AKT of Ad-GFP-infected without palmitate-treated cells was set to 100, and the others were expressed as its relative values. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 3, *P < 0.05 vs Ad-GFP with insulin/Veh, # P < 0.05 vs Ad-GFP with insulin/palmitate, by ANOVA. (G and H) C2C12 myotubes were infected with Ad-HA-ACSL1wt, Ad-HA-ACSL1mt, or Ad-GFP (100 moi) for 24 h, and then intracellular TG (G) and DAG (H) levels were measured. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 5 (TG), n = 3 (DAG), *P < 0.05 vs Veh, # P < 0.05 vs Ad-GFP/Palmitate, by ANOVA.