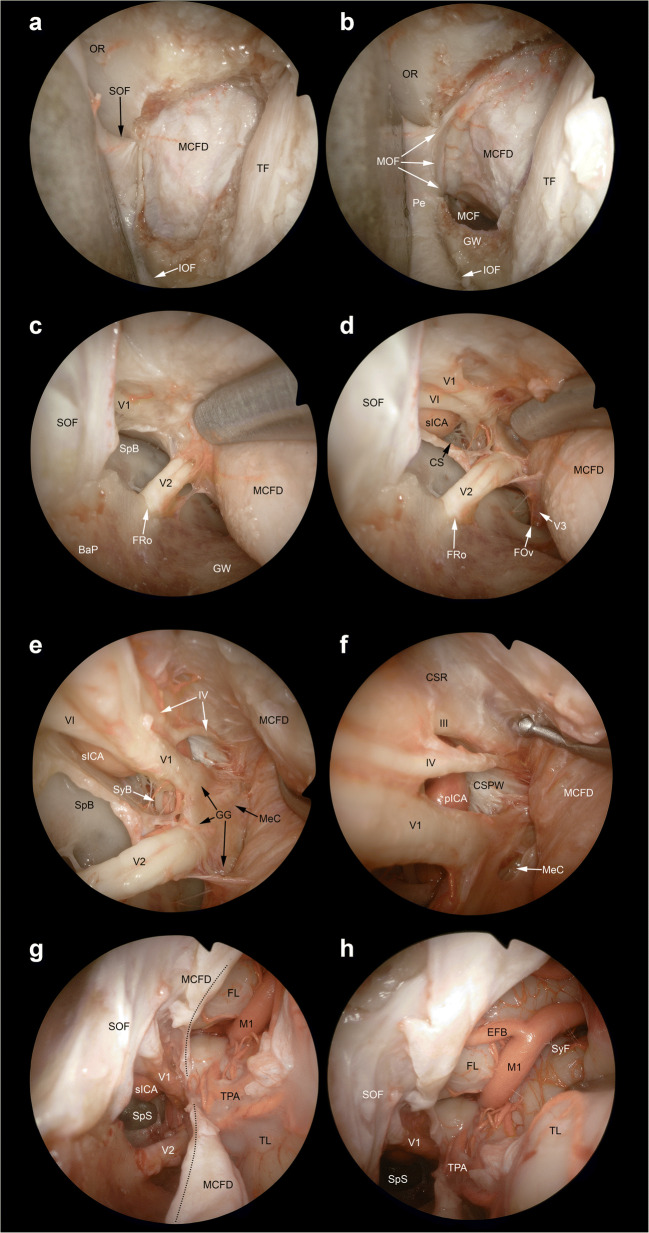
Fig. 8.
Transorbital exposure of the lateral middle skull base, parasellar area, and Sylvian fissure. A The middle cranial fossa dura (MCFD) can be exposed through a craniectomy in the area between the superior orbital fissure (SOF) and inferior orbital fissure (IOF). This portion of the skull base can be exposed through both the superior eyelid crease approach and lateral retrocanthal approach. The former provides a slightly descending trajectory towards the middle cranial fossa (MCF), whereas the latter route is parallel to the plane of the horizontal portion of the greater sphenoidal wing (GW). B The meningo-orbital fold (MOF) is identified as the line where the dura of the middle and anterior cranial fosse merge with the periorbit. C Epidural dissection along the middle cranial fossa allows exposure of the oftalmic (V1) and the maxillary (V2) branches of the trigeminal nerve, which run towards the superior orbital fissure and foramen rotundum (FRo), respectively. D Interdural dissection above the trigeminal branches provides access to the parasellar area and allows identification of the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V3) and foramen ovale (FOv). The cavernous sinus (CS) is identified above the ophthalmic nerve (i.e., infratrochlear or Parkinson’s triangle) and in the space between the ophthalmic and maxillary nerves (i.e., anteromedial or Mullan’s triangle) and the parasellar tract of the internal carotid artery (sICA), abducens nerve (VI), and trochlear nerve (IV) are exposed. E Further posterior interdural dissection exposes the Gasserian ganglion (GG) and Meckel’s cave (MeC). F The oculomotor nerve (III), cavernous sinus roof (CSR), posterior wall of the cavernous sinus (PWCS), and paraclival portion of the internal carotid artery (pICA) can be identified by further elevating the dura propria of the parasellar area. G The dura propria of the parasellar area and lateral middle cranial base is incised (black dotted line) to access the intradural compartment Sylvian fissure (SyF). H The first tract of the middle cerebral artery (M1), early frontal branch (EFB), and temporal polar arteries (TPA) are identified between the frontal (FL) and temporal lobe (TL). BaP, base of the pterygoid process; OR, orbital roof; Pe, periorbit; SyB, sympathetic branch of the abducens nerve; SpB, sphenoid body; TF, Temporal fossa