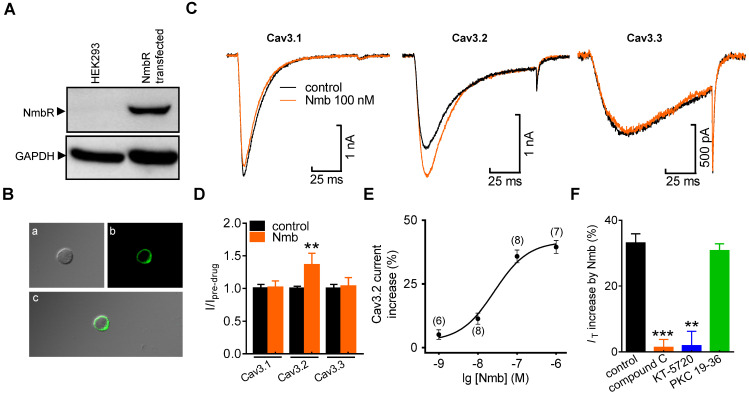
Figure 5.
Activation of NmbR stimulates recombinant Cav3.2 channels heterologously expressed in HEK293 cells. A, western blot analysis of NmbR in HEK293 cells transiently transfected with NmbR cDNA. Blots depicted are representative of three independent experiments. B, membrane localization of NmbR in transfected HEK293 cells. Alphabets a through c in the diagram indicate the differential interference contrast (DIC, a), the EGFP fluorescent signals of NmbR (b), and the merged image (c), respectively. C, exemplary current traces show the effect of Nmb (100 nM) on Cav3.1 (α1G), Cav3.2 (α1H) and Cav3.3 (α1I) channel currents. Currents were elicited by a 100 ms depolarizing step pulse from the holding potential of -110 mV to -30 mV. D, summary data show the effect of 100 nM Nmb on Cav3.1 (n = 10), Cav3.2 (n = 9) and Cav3.3 (n = 7) channel currents. **p < 0.01 versus control, two-tailed t test. E, dose-dependent effects of Nmb on Cav3.2 channel currents. Solid line represents the sigmoidal dose-response fits. Numbers in parentheses denote n cells tested at each concentration. F, summary data show the effect of Nmb (100 nM) on Cav3.2 channel currents in cells pre-incubated with 10 µM compound C (n = 8), in cells pretreated with 1 µM KT-5720 (n = 9), and in cells dialyzed with 10 μM PKC 19-36 (n = 9), respectively. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 versus control, two-tailed t test.